Mitochondrial Isolevuglandins Contribute to Vascular Oxidative Stress and Mitochondria-Targeted Scavenger of Isolevuglandins Reduces Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Hypertension
- PMID: 33012204
- PMCID: PMC7666054
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15236
Mitochondrial Isolevuglandins Contribute to Vascular Oxidative Stress and Mitochondria-Targeted Scavenger of Isolevuglandins Reduces Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Hypertension
Abstract
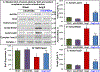
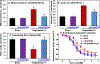
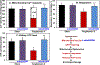
Hypertension remains a major health problem in Western Societies, and blood pressure is poorly controlled in a third of patients despite use of multiple drugs. Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to hypertension, and mitochondria-targeted agents can potentially improve treatment of hypertension. We have proposed that mitochondrial oxidative stress produces reactive dicarbonyl lipid peroxidation products, isolevuglandins, and that scavenging of mitochondrial isolevuglandins improves vascular function and reduces hypertension. To test this hypothesis, we have studied the accumulation of mitochondrial isolevuglandins-protein adducts in patients with essential hypertension and Ang II (angiotensin II) model of hypertension using mass spectrometry and Western blot analysis. The therapeutic potential of targeting mitochondrial isolevuglandins was tested by the novel mitochondria-targeted isolevuglandin scavenger, mito2HOBA. Mitochondrial isolevuglandins in arterioles from hypertensive patients were 250% greater than in arterioles from normotensive subjects, and ex vivo mito2HOBA treatment of arterioles from hypertensive subjects increased deacetylation of a key mitochondrial antioxidant, SOD2 (superoxide dismutase 2). In human aortic endothelial cells stimulated with Ang II plus TNF (tumor necrosis factor)-α, mito2HOBA reduced mitochondrial superoxide and cardiolipin oxidation, a specific marker of mitochondrial oxidative stress. In Ang II-infused mice, mito2HOBA diminished mitochondrial isolevuglandins-protein adducts, raised Sirt3 (sirtuin 3) mitochondrial deacetylase activity, reduced vascular superoxide, increased endothelial nitric oxide, improved endothelium-dependent relaxation, and attenuated hypertension. Mito2HOBA preserved mitochondrial respiration, protected ATP production, and reduced mitochondrial permeability pore opening in Ang II-infused mice. These data support the role of mitochondrial isolevuglandins in endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. We conclude that scavenging of mitochondrial isolevuglandins may have therapeutic potential in treatment of vascular dysfunction and hypertension.
Keywords: Sirtuin 3; blood pressure; mitochondria; oxidative stress; superoxide dismutase.
Figures

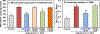

References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223 - PubMed
-
- Sacco RL, Benjamin EJ, Broderick JP, Dyken M, Easton JD, Feinberg WM, Goldstein LB, Gorelick PB, Howard G, Kittner SJ, Manolio TA, Whisnant JP, Wolf PA. American heart association prevention conference. Iv. Prevention and rehabilitation of stroke Risk factors. Stroke 1997;28:1507–1517 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

