COVID-19 and Sex Differences: Mechanisms and Biomarkers
- PMID: 33012349
- PMCID: PMC7402208
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.07.024
COVID-19 and Sex Differences: Mechanisms and Biomarkers
Abstract
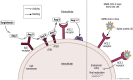
Men are consistently overrepresented in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severe outcomes, including higher fatality rates. These differences are likely due to gender-specific behaviors, genetic and hormonal factors, and sex differences in biological pathways related to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Several social, behavioral, and comorbid factors are implicated in the generally worse outcomes in men compared with women. Underlying biological sex differences and their effects on COVID-19 outcomes, however, have received less attention. The present review summarizes the available literature regarding proposed molecular and cellular markers of COVID-19 infection, their associations with health outcomes, and any reported modification by sex. Biological sex differences characterized by such biomarkers exist within healthy populations and also differ with age- and sex-specific conditions, such as pregnancy and menopause. In the context of COVID-19, descriptive biomarker levels are often reported by sex, but data pertaining to the effect of patient sex on the relationship between biomarkers and COVID-19 disease severity/outcomes are scarce. Such biomarkers may offer plausible explanations for the worse COVID-19 outcomes seen in men. There is the need for larger studies with sex-specific reporting and robust analyses to elucidate how sex modifies cellular and molecular pathways associated with SARS-CoV-2. This will improve interpretation of biomarkers and clinical management of COVID-19 patients by facilitating a personalized medical approach to risk stratification, prevention, and treatment.
Copyright © 2020 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bhopal R. Covid-19 worldwide: we need precise data by age group and sex urgently. BMJ. 2020;369:m1366. - PubMed
-
- Global Health 50/50. Sex, Gender and Covid-19. Vol 20202020: Sex, Gender and COVID-19. 2020. https://globalhealth5050.org/covid19/sex-disaggregated-data-tracker/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

