Dangers of delayed diagnosis of perianal abscess and undrained perianal sepsis in Fournier's gangrene: a case series
- PMID: 33012714
- PMCID: PMC7536776
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-236503
Dangers of delayed diagnosis of perianal abscess and undrained perianal sepsis in Fournier's gangrene: a case series
Abstract
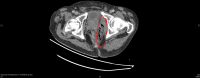
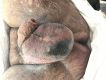
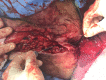
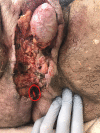
Fournier's gangrene (FG) is a rapidly progressing infective necrotising fasciitis of the perianal, perineal and genital region. It is characterised by its aggressive nature and high mortality rates of between 15% and 50%. While it has been commonly found to primarily develop from urological sources, there have been increasing reports of the role of colorectal sources as the underlying aetiology of FG. Presented is a case series of four FG presentations at a single institution during a 12-month period as a result of underlying untreated perianal disease highlighting its dangers in progressing to a deadly infection, advocating for early and aggressive surgical debridement, and the role of adjunct scoring systems, such as Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotising Fasciitis, in guiding clinical diagnosis.
Keywords: general surgery; infectious diseases.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Baurienne H. Sur une plaie contuse qui s’est terminee par le sphacele de le scrotum. J Med Chir Pharm 1764;20:251–6.
-
- Fournier JA. Gangrene foudroyante de la verge. Medecin Pratique 1883;4:589–97.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
