Effect of modified ultrafiltration on cytokines and hemoconcentration in dogs undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass
- PMID: 33012753
- PMCID: PMC7719890
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.20-0143
Effect of modified ultrafiltration on cytokines and hemoconcentration in dogs undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass
Abstract
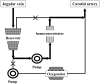
Cardiac surgery using cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) generates severe inflammatory reactions secondary to hemodilution and surgical stress. This study was conducted to evaluate whether modified ultrafiltration (MUF) could be performed safely and to clarify its effects during mitral valve repair in dogs in terms of hemodilution and the status of inflammatory cytokines. We retrospectively studied 38 dogs with mitral valve disease who underwent MUF immediately after mitral valve repair under CPB. To determine the effect of MUF, we measured the pre- and post-MUF blood dilution and blood cytokine levels. The levels of red blood cells, hematocrit (HCT), and albumin were significantly increased after MUF, whereas interleukin (IL)-6 levels were significantly increased from 24.3 (range 9.6-54.6) to 32.3 (15.9-65.1) pg/ml. The levels of IL-8 and IL-10 declined significantly after MUF, from 368.2 (246.1-669.4) and 45.4 (28.6-76.1) to 272.2 (174.1-414.4) and 28.8 (18.8-44.5) pg/ml, respectively. Our results demonstrated that MUF can be applied in dogs undergoing CPB and is effective in achieving hemoconcentration. Moreover, MUF may be useful for the removal of cytokines. Further studies are needed to validate these findings and clarify the effects of inflammatory cytokines after CPB.
Keywords: cardiopulmonary bypass; cytokine; mitral valvuloplasty; modified ultrafiltration.
Figures
References
-
- Atkins B. Z., Danielson D. S., Fitzpatrick C. M., Dixon P., Petersen R. P., Carpenter A. J.2010. Modified ultrafiltration attenuates pulmonary-derived inflammatory mediators in response to cardiopulmonary bypass. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 11: 599–603. doi: 10.1510/icvts.2010.234344 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bando K., Turrentine M. W., Vijay P., Sharp T. G., Sekine Y., Lalone B. J., Szekely L., Brown J. W.1998. Effect of modified ultrafiltration in high-risk patients undergoing operations for congenital heart disease. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 66: 821–827, discussion 828. doi: 10.1016/S0003-4975(98)00606-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Borgarelli M., Abbott J., Braz-Ruivo L., Chiavegato D., Crosara S., Lamb K., Ljungvall I., Poggi M., Santilli R. A., Haggstrom J.2015. Prevalence and prognostic importance of pulmonary hypertension in dogs with myxomatous mitral valve disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 29: 569–574. doi: 10.1111/jvim.12564 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buchholz B. J., Bert A. A., Price D. R., Hopkins R. A., Stearns G. T.1999. Veno-arterial modified ultrafiltration in children after cardiopulmonary bypass. J. Extra Corpor. Technol. 31: 47–49. - PubMed