COVID-19 and the rise of intimate partner violence
- PMID: 33012955
- PMCID: PMC7522673
- DOI: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105217
COVID-19 and the rise of intimate partner violence
Abstract
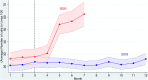
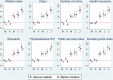
Stay-at-home policies have been implemented worldwide to reduce the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. However, there is a growing concern that such policies could increase violence against women. We find evidence in support of this critical concern. We focus on Peru, a country that imposed a strict nationwide lockdown starting in mid-March and where nearly 60% of women already experienced violence before COVID-19. Using administrative data on phone calls to the helpline for domestic violence (Línea 100), we find that the incidence rate of the calls increased by 48 percent between April and July 2020, with effects increasing over time. The rise in calls is found across all states and it is not driven by baseline characteristics, including previous prevalence of violence against women. These findings create the need to identify policies to mitigate the negative impact of stay-at-home orders on women's safety.
Keywords: COVID-19; Domestic violence; Intimate partner violence; Lockdowns; Peru.
© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Agüero, J. M. (2019). Information and Behavioral Responses with More than One Agent: The Case of Domestic Violence Awareness Campaigns (No. 2019-04). University of Connecticut, Department of Economics
-
- Alon, T. M., Doepke, M., Olmstead-Rumsey, J. & Tertilt, M. (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on gender equality (No. w26947). National Bureau of Economic Research
-
- Bott S., Guedes A., Goodwin M.M., Mendoza J.A. Pan American Health Organization; Washington, DC: 2012. Violence against women in Latin America and the Caribbean: A comparative analysis of population-based data from 12 countries.
-
- Brown, C. S., Ravallion, M. & Van De Walle, D. (2020). Can the World’s Poor Protect Themselves from the New Coronavirus? (No. w27200). National Bureau of Economic Research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
