MIPs for commercial application in low-cost sensors and assays - An overview of the current status quo
- PMID: 33012991
- PMCID: PMC7525251
- DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.128973
MIPs for commercial application in low-cost sensors and assays - An overview of the current status quo
Abstract
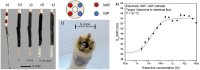
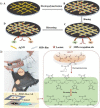
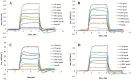
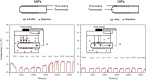
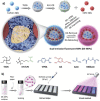
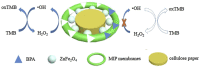
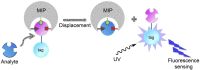
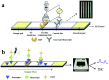
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) have emerged over the past few decades as interesting synthetic alternatives due to their long-term chemical and physical stability and low-cost synthesis procedure. They have been integrated into many sensing platforms and assay formats for the detection of various targets, ranging from small molecules to macromolecular entities such as pathogens and whole cells. Despite the advantages MIPs have over natural receptors in terms of commercialization, the striking success stories of biosensor applications such as the glucose meter or the self-test for pregnancy have not been matched by MIP-based sensor or detection kits yet. In this review, we zoom in on the commercial potential of MIP technology and aim to summarize the latest developments in their commercialization and integration into sensors and assays with high commercial potential. We will also analyze which bottlenecks are inflicting with commercialization and how recent advances in commercial MIP synthesis could overcome these obstacles in order for MIPs to truly achieve their commercial potential in the near future.
Keywords: Biosensing; Commercialization; Diagnostics; Lateral flow assays; Molecularly imprinted polymers.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no declarations of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Newman J.D., Turner A.P.F. Home blood glucose biosensors: a commercial perspective. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005;20(12):2435–2453. - PubMed
-
- Fan Y., Zeng G., Ma X. Effects of prepolymerization on surface molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid separation and analysis of sulfonamides in water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;571:21–29. - PubMed
-
- Lowdon J.W., Alkirkit S.M.O., Mewis R.E., Fulton D., Banks C.E., Sutcliffe O.B., Peeters M. Engineering molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) for the selective extraction and quantification of the novel psychoactive substance (NPS) methoxphenidine and its regioisomers. Analyst. 2018;143:2081–2089. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
