The Nephroprotective Effect of Lycopene on Renal Ischemic Reperfusion Injury: A Mouse Model
- PMID: 33013018
- PMCID: PMC7502648
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-019-00848-7
The Nephroprotective Effect of Lycopene on Renal Ischemic Reperfusion Injury: A Mouse Model
Abstract
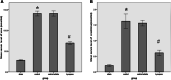
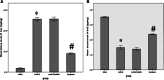
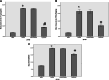
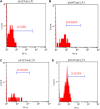
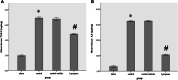
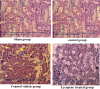
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is characterized by fast decline in renal function within a short period of time. Renal ischemic-reperfusion (I-R) injury is the main cause of AKI. This study aims to investigate the possible nephroprotective effect of lycopene on renal ischemic-reperfusion injury in mice model. Forty Swiss Albino adult male mice were randomly allocated onto one of the four study groups: sham group: mice had median laparotomy under anesthesia with no procedures performed, renal tissues and blood samples were collected. ischemic-reperfusion group (I-R-control): mice underwent median laparotomy under anesthesia, followed by 30 min bilateral renal ischemia. Renal tissues and blood samples were collected after 2 h from reperfusion. Vehicle-treated group: mice were pretreated with intra 1% dimethyl sulfoxide 30 min before inducing ischemia. Lycopene-treated group: mice were pretreated with 10 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection of lycopene 30 min before inducing renal ischemia. Renal tissues, and blood samples were collected after 2 h from reperfusion. Blood and tissue samples were collected to look for evidence of inflammation and necrosis. Blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine as well as plasma NGAL levels were significantly increased in the active control group (P ≤ 0.05), when compared to the sham group. Similarly, renal levels of Notch2/Hes 1, TLR 2, IL-6, Bax, and F2-isoprostane were significantly increased in the active control group as compared to the sham group (P ≤ 0.05). Moreover, lycopene treatment was found to be significantly effective in reducing the increased levels of these markers after I-R injury (P ≤ 0.05).
Keywords: IL-6; Lycopene; NF-κB; Notch2/hes1 protein; Renal ischemia–reperfusion injury.
© Association of Clinical Biochemists of India 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
