State-dependent memory and its modulation by different brain areas and neurotransmitters
- PMID: 33013265
- PMCID: PMC7527511
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2020-2612
State-dependent memory and its modulation by different brain areas and neurotransmitters
Abstract
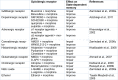
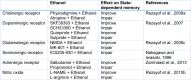
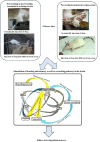
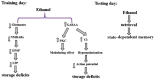
The state-dependent memory defines as a state that the retrieval of recently obtained information may be potential if the subject exists in a similar physiological situation as for the period of the encoding stage. Studies revealed that exogenous and endogenous compounds could induce state-dependent memory. The state-dependent memory made it probable to differentiate the effects of drugs per se on learning from the effects due to alterations in drug state during the task. Studies proposed the role of regions beyond the limbic formation and illustrated that state-dependent memory produced by various neurotransmitter systems and pharmacological compounds. Our review of the literature revealed that: (a) re-administration of drugs on the same state induce state-dependent memory; (b) many neurotransmitters induce endogenous state-dependent memory; (c) there are cross state-dependent learning and memory between some drugs; (d) some sites of the brain including the CA1 areas of the hippocampus, central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA), septum, ventral tegmental area (VTA), and nucleus accumbens (NAC) are involved in state-dependent memory. See also Figure 1(Fig. 1).
Keywords: CA1; CeA; neurotransmitter; pharmacological compounds; state-dependent memory.
Copyright © 2020 Zarrindast et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional correlation between GABAergic and dopaminergic systems of dorsal hippocampus and ventral tegmental area in passive avoidance learning in rats.Neuroscience. 2011 Nov 24;196:104-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.08.073. Epub 2011 Sep 10. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21925239
-
Involvement of central amygdala NMDA receptor mechanism in morphine state-dependent memory retrieval.Neurosci Res. 2011 Jan;69(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2010.09.005. Epub 2010 Sep 25. Neurosci Res. 2011. PMID: 20875463
-
Food reward-induced neurotransmitter changes in cognitive brain regions.Neurochem Res. 2007 Oct;32(10):1772-82. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9343-8. Epub 2007 Aug 25. Neurochem Res. 2007. PMID: 17721820
-
Dopaminergic and cholinergic learning mechanisms in nicotine addiction.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 Sep;1349(1):46-63. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12871. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 26301866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Localization of brain reinforcement mechanisms: intracranial self-administration and intracranial place-conditioning studies.Behav Brain Res. 1999 Jun;101(2):129-52. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(99)00022-4. Behav Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10372570 Review.
Cited by
-
Benzodiazepine-induced anterograde amnesia: detrimental side effect to novel study tool.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 14;14:1257030. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1257030. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37781704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross state-dependent memory retrieval between tramadol and ethanol: involvement of dorsal hippocampal GABAA receptors.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Jan;241(1):139-152. doi: 10.1007/s00213-023-06469-6. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 37758936
-
A proposed mechanism for the MDMA-mediated extinction of traumatic memories in PTSD patients treated with MDMA-assisted therapy.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Oct 12;13:991753. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.991753. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36311515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intervention for Cognitive Reserve Enhancement in Delaying the Onset of Alzheimer's Symptomatic Expression (INCREASE) Study: Results from a Randomized Controlled Study of Medication Therapy Management Targeting a Delay in Prodromal Dementia Symptom Progression.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2022;9(4):646-654. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2022.55. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2022. PMID: 36281668 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A neuropeptide signal confers ethanol state dependency during olfactory learning in Caenorhabditis elegans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Nov 16;119(46):e2210462119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2210462119. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36343256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmadi S, Zarrindast MR, Nouri M, Haeri-Rohani A, Rezayof A. N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the ventral tegmental area are involved in retrieval of inhibitory avoidance memory by nicotine. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2007;88:352–358. - PubMed
-
- Alijanpour S, Rezayof A. Involvement of dorsal hippocampal and medial septal nicotinic receptors in cross state-dependent memory between WIN55, 212-2 and nicotine or ethanol in mice. Neuroscience. 2013;245:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Ardjmand A, Rezayof A, Zarrindast MR. Involvement of central amygdala NMDA receptor mechanism in morphine state-dependent memory retrieval. Neurosci Res. 2011;69:25–31. - PubMed
-
- Azami NS, Piri M, Oryan S, Jahanshahi M, Babapour V, Zarrindast MR. Involvement of dorsal hippocampal alpha-adrenergic receptors in the effect of scopolamine on memory retrieval in inhibitory avoidance task. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010;93:455–462. - PubMed
-
- Azizbeigi R, Ahmadi S, Babapour V, Rezayof A, Zarrindast MR. Nicotine restores morphine-induced memory deficit through the D1 and D2 dopamine receptor mechanisms in the nucleus accumbens. J Psychopharmacol. 2011;25:1126–1133. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
