State-dependent memory and its modulation by different brain areas and neurotransmitters
- PMID: 33013265
- PMCID: PMC7527511
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2020-2612
State-dependent memory and its modulation by different brain areas and neurotransmitters
Abstract
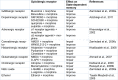
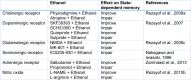
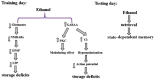
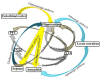
The state-dependent memory defines as a state that the retrieval of recently obtained information may be potential if the subject exists in a similar physiological situation as for the period of the encoding stage. Studies revealed that exogenous and endogenous compounds could induce state-dependent memory. The state-dependent memory made it probable to differentiate the effects of drugs per se on learning from the effects due to alterations in drug state during the task. Studies proposed the role of regions beyond the limbic formation and illustrated that state-dependent memory produced by various neurotransmitter systems and pharmacological compounds. Our review of the literature revealed that: (a) re-administration of drugs on the same state induce state-dependent memory; (b) many neurotransmitters induce endogenous state-dependent memory; (c) there are cross state-dependent learning and memory between some drugs; (d) some sites of the brain including the CA1 areas of the hippocampus, central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA), septum, ventral tegmental area (VTA), and nucleus accumbens (NAC) are involved in state-dependent memory. See also Figure 1(Fig. 1).
Keywords: CA1; CeA; neurotransmitter; pharmacological compounds; state-dependent memory.
Copyright © 2020 Zarrindast et al.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmadi S, Zarrindast MR, Nouri M, Haeri-Rohani A, Rezayof A. N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the ventral tegmental area are involved in retrieval of inhibitory avoidance memory by nicotine. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2007;88:352–358. - PubMed
-
- Alijanpour S, Rezayof A. Involvement of dorsal hippocampal and medial septal nicotinic receptors in cross state-dependent memory between WIN55, 212-2 and nicotine or ethanol in mice. Neuroscience. 2013;245:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Ardjmand A, Rezayof A, Zarrindast MR. Involvement of central amygdala NMDA receptor mechanism in morphine state-dependent memory retrieval. Neurosci Res. 2011;69:25–31. - PubMed
-
- Azami NS, Piri M, Oryan S, Jahanshahi M, Babapour V, Zarrindast MR. Involvement of dorsal hippocampal alpha-adrenergic receptors in the effect of scopolamine on memory retrieval in inhibitory avoidance task. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010;93:455–462. - PubMed
-
- Azizbeigi R, Ahmadi S, Babapour V, Rezayof A, Zarrindast MR. Nicotine restores morphine-induced memory deficit through the D1 and D2 dopamine receptor mechanisms in the nucleus accumbens. J Psychopharmacol. 2011;25:1126–1133. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
