Therapeutic Potential of Centella asiatica and Its Triterpenes: A Review
- PMID: 33013406
- PMCID: PMC7498642
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.568032
Therapeutic Potential of Centella asiatica and Its Triterpenes: A Review
Abstract
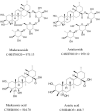
Centella asiatica (also known as Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. or Gotu kola) is a traditional Chinese medicine with extensive medicinal value, which is commonly used in Southeast Asian countries. This study aimed to summarize the effects of C. asiatica and its main components on neurological diseases, endocrine diseases, skin diseases, cardiovascular diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, immune diseases, and gynecological diseases, as well as potential molecular mechanisms, to study the pathological mechanism of these diseases based on the changes at the molecular level. The results showed that C. asiatica and its triterpenoids had extensive beneficial effects on neurological and skin diseases, which were confirmed through clinical studies. They exhibited anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative stress, anti-apoptotic effects, and improvement in mitochondrial function. However, further clinical studies are urgently required due to the low level of evidence and lack of patients.
Keywords: Centella asiatica; anti-apoptosis; anti-inflammatory; anti-oxidative stress; triterpenoids.
Copyright © 2020 Sun, Wu, Wu, Zhang, Qin, Hayashi, Kudo, Gao and Liu.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmad Rather M., Justin-Thenmozhi A., Manivasagam T., Saravanababu C., Guillemin G. J., Essa M. M. (2019). Asiatic Acid Attenuated Aluminum Chloride-Induced Tau Pathology, Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Via AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway in Wistar Rats. Neurotox. Res. 35 (4), 955–968. 10.1007/s12640-019-9999-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources