Type I PRMT Inhibition Protects Against C9ORF72 Arginine-Rich Dipeptide Repeat Toxicity
- PMID: 33013410
- PMCID: PMC7508178
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.569661
Type I PRMT Inhibition Protects Against C9ORF72 Arginine-Rich Dipeptide Repeat Toxicity
Abstract
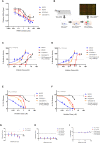
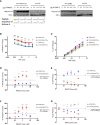
Repeat expansion mutations in the C9ORF72 gene are the most common genetic cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Repeat-associated non-AUG translation of this expansion produces dipeptide repeat proteins (DRPs). The arginine containing DRPs, polyGR and polyPR, are consistently reported to be the most toxic. Here we demonstrated that small molecule inhibition of type I protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMT) protects against polyGR and polyPR toxicity. Furthermore, our findings suggest that asymmetric dimethylation of polyGR and polyPR by Type I PRMTs plays important roles in their cytotoxicity.
Keywords: ALS (Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis); C9ORF72 DPRs; FTD (Fronto-Temporal Dementia); arginine methylation; glycine-arginine; proline-arginine; protein arginine methyl transferase.
Copyright © 2020 Premasiri, Gill and Vieira.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

