Exogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Within the Nucleus Ambiguus Inhibits Gastrointestinal Motility in Rats
- PMID: 33013478
- PMCID: PMC7516268
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.545184
Exogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Within the Nucleus Ambiguus Inhibits Gastrointestinal Motility in Rats
Abstract
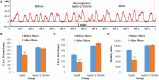
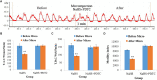
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a neuromodulator in the central nervous system. However, the physiological role of H2S in the nucleus ambiguus (NA) has rarely been reported. This research aimed to elucidate the role of H2S in the regulation of gastrointestinal motility in rats. Male Wistar rats were randomly assigned to sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS; 4 and 8 nmol) groups, physiological saline (PS) group, capsazepine (10 pmol) + NaHS (4 nmol) group, L703606 (4 nmol) + NaHS (4 nmol) group, and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC, 4 nmol) + NaHS (4 nmol) group. Gastrointestinal motility curves before and after the injection were recorded using a latex balloon attached with a pressure transducer, which was introduced into the pylorus through gastric fundus. The results demonstrated that NaHS (4 and 8 nmol), an exogenous H2S donor, remarkably suppressed gastrointestinal motility in the NA of rats (P < 0.01). The suppressive effect of NaHS on gastrointestinal motility could be prevented by capsazepine, a transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) antagonist, and PDTC, a NF-κB inhibitor. However, the same amount of PS did not induce significant changes in gastrointestinal motility (P > 0.05). Our findings indicate that NaHS within the NA can remarkably suppress gastrointestinal motility in rats, possibly through TRPV1 channels and NF-κB-dependent mechanism.
Keywords: NF-κB; TRPV1; gastric motility; hydrogen sulfide; nucleus ambiguus.
Copyright © 2020 Sun, Ding, Shi, Li, Jin, Yang, Chen, Tian, Zhu and Sun.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

