Difference Between Intentional and Reactive Movement in Side-Steps: Patterns of Temporal Structure and Force Exertion
- PMID: 33013564
- PMCID: PMC7495094
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.02186
Difference Between Intentional and Reactive Movement in Side-Steps: Patterns of Temporal Structure and Force Exertion
Abstract
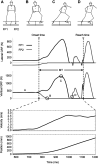
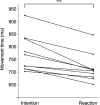
Intentional and reactive movements are dissimilar in terms of execution time. Previous studies reported that reactive movements are faster than intentional movements ("Bohr's law" or "Gunslinger effect"), however, these studies focused only on hand-reaching tasks, such as pressing buttons. No studies assessed whole-body movements involving movement of the center of mass (CoM). This movement is characterized by many degrees of freedom because it involves many joints and requires more force than the hand-reaching movement. In this study, we determined the differences in the patterns of temporal structure and force exertion to elucidate the mechanism of "Bohr's law" in whole-body movement involving movement of the CoM. Ten participants performed a sidestepping task, which requires at least two steps: (1) an intentional movement, in which the movement started with the participants' own timing; and (2) a reactive movement, in which the movement started the moment a light-emitting diode bulb in front of the participants lit up. We collected data on the ground reaction forces and coordinates of 20 body points. The time of movement onset was calculated and defined based on the ground reaction force, which has the earliest onset compared with velocity and position. The execution time was significantly shorter in the reactive movement condition than in the intentional movement condition (772 vs. 715 ms, p = 2.9 × 10-4). We confirmed that Bohr's law was applicable not only in hand-reaching tasks but also in whole-body movement. Moreover, we identified three phases, including the velocity reversal phenomenon associated with the produced mechanism of Bohr's law, and provided the temporal structure. The difference in the pattern of force exertion accompanying the two styles of motor planning with different accuracies was strongly associated with this motor characteristic. These findings may serve as important basic data to scientifically clarify the mechanism of complex physical tactics implemented in one-on-one dueling in various sports.
Keywords: externally triggered movement; internally initiated movement; kinetics; movement time; onset time; whole body.
Copyright © 2020 Wakatsuki and Yamada.
Figures



References
-
- Ae M., Tang H., Yokoi T. (1992). Estimation of inertia properties of the body segments in Japanese athletes. Biomechanisms 11 23–33. 10.3951/biomechanisms.11.23 - DOI
-
- Cañal-Bruland R. (2009). Visual cueing in sport-specific decision making. Int. J. Sport Exer. Psychol. 7 450–464. 10.1080/1612197X.2009.9671919 - DOI
-
- Cline B. L. (1987). Men Who Made a New Physics: Physicists and the Quantum Theory. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

