Consensus-Based Core Set of Outcome Measures for Clinical Motor Rehabilitation After Stroke-A Delphi Study
- PMID: 33013624
- PMCID: PMC7496361
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00875
Consensus-Based Core Set of Outcome Measures for Clinical Motor Rehabilitation After Stroke-A Delphi Study
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Consensus-Based Core Set of Outcome Measures for Clinical Motor Rehabilitation After Stroke-A Delphi Study.Front Neurol. 2021 May 27;12:697935. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.697935. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34122324 Free PMC article.
Abstract
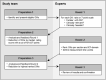
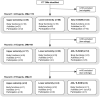
Introduction: Outcome measures are key to tailor rehabilitation goals to the stroke patient's individual needs and to monitor poststroke recovery. The large number of available outcome measures leads to high variability in clinical use. Currently, an internationally agreed core set of motor outcome measures for clinical application is lacking. Therefore, the goal was to develop such a set to serve as a quality standard in clinical motor rehabilitation poststroke. Methods: Outcome measures for the upper and lower extremities, and activities of daily living (ADL)/stroke-specific outcomes were identified and presented to stroke rehabilitation experts in an electronic Delphi study. In round 1, clinical feasibility and relevance of the outcome measures were rated on a 7-point Likert scale. In round 2, those rated at least as "relevant" and "feasible" were ranked within the body functions, activities, and participation domains of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF). Furthermore, measurement time points poststroke were indicated. In round 3, answers were reviewed in reference to overall results to reach final consensus. Results: In total, 119 outcome measures were presented to 33 experts from 18 countries. The recommended core set includes the Fugl-Meyer Motor Assessment and Action Research Arm Test for the upper extremity section; the Fugl-Meyer Motor Assessment, 10-m Walk Test, Timed-Up-and-Go, and Berg Balance Scale for the lower extremity section; and the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, and Barthel Index or Functional Independence Measure for the ADL/stroke-specific section. The Stroke Impact Scale was recommended spanning all ICF domains. Recommended measurement time points are days 2 ± 1 and 7; weeks 2, 4, and 12; 6 months poststroke and every following 6th month. Discussion and Conclusion: Agreement was found upon a set of nine outcome measures for application in clinical motor rehabilitation poststroke, with seven measurement time points following the stages of poststroke recovery. This core set was specifically developed for clinical practice and distinguishes itself from initiatives for stroke rehabilitation research. The next challenge is to implement this clinical core set across the full stroke care continuum with the aim to improve the transparency, comparability, and quality of stroke rehabilitation at a regional, national, and international level.
Keywords: Delphi study; clinical; motor rehabilitation; outcome measures; stroke.
Copyright © 2020 Pohl, Held, Verheyden, Alt Murphy, Engelter, Flöel, Keller, Kwakkel, Nef, Ward, Luft and Veerbeek.
Figures
Similar articles
-
International consensus recommendations for outcome measurement in post-stroke arm rehabilitation trials.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2021 Feb;57(1):61-68. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.20.06575-2. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2021. PMID: 33215905
-
European evidence-based recommendations for clinical assessment of upper limb in neurorehabilitation (CAULIN): data synthesis from systematic reviews, clinical practice guidelines and expert consensus.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021 Nov 8;18(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12984-021-00951-y. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 34749752 Free PMC article.
-
A proposal for an Italian minimum data set assessment protocol for robot-assisted rehabilitation: a Delphi study.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2015 Dec;51(6):745-53. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2015. PMID: 26138089
-
Standardized measurement of balance and mobility post-stroke: Consensus-based core recommendations from the third Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Roundtable.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2024 Jan;38(1):41-51. doi: 10.1177/15459683231209154. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2024. PMID: 37837351 Review.
-
Effects of Robot-Assisted Therapy for the Upper Limb After Stroke.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2017 Feb;31(2):107-121. doi: 10.1177/1545968316666957. Epub 2016 Sep 24. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2017. PMID: 27597165 Review.
Cited by
-
A reliable and valid assessment of upper limb movement quality after stroke: the observational Drinking Task Assessment.J Rehabil Med. 2024 Oct 9;56:jrm40362. doi: 10.2340/jrm.v56.40362. J Rehabil Med. 2024. PMID: 39382398 Free PMC article.
-
Spectral exponent assessment and neurofilament light chain: a comprehensive approach to describe recovery patterns in stroke.Front Neurol. 2024 Mar 18;15:1329044. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1329044. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38562428 Free PMC article.
-
Responsiveness and construct validity of two outcome measures of bilateral upper limb function in patients with chronic stroke.Front Neurol. 2024 May 23;15:1352365. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1352365. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38846043 Free PMC article.
-
Standardized tools for assessing balance and mobility in stroke clinical practice guidelines worldwide: A scoping review.Front Rehabil Sci. 2023 Feb 21;4:1084085. doi: 10.3389/fresc.2023.1084085. eCollection 2023. Front Rehabil Sci. 2023. PMID: 36896249 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal and multidomain lesion network mapping enhances prediction of sensorimotor behavior in stroke patients.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 27;12(1):22400. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26945-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36575263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franceschini M, Porta FL, Agosti M, Massucci M. Is health-related-quality of life of stroke patients influenced by neurological impairments at 1 year after stroke? Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. (2010) 46:11. - PubMed

