Comparing Programming Sessions of Vim-DBS
- PMID: 33013651
- PMCID: PMC7494809
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00987
Comparing Programming Sessions of Vim-DBS
Abstract
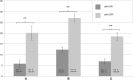
Background: Essential Tremor (ET) is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by postural and kinetic tremor most commonly affecting the hands and arms. Medically intractable ET can be treated by deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the ventral intermediate nucleus of thalamus (VIM). We investigated whether the location of the effective contact (most tremor suppression with at least side effects) in VIM-DBS for ET changes over time, indicating a distinct mechanism of loss of efficacy that goes beyond progression of tremor severity, or a mere reduction of DBS efficacy. Methods: We performed programming sessions in 10 patients who underwent bilateral vim-DBS surgery between 2009 and 2017 at our department. In addition to the intraoperative (T1) and first clinical programming session (T2) a third programming session (T3) was performed to assess the effect- and side effect threshold (minimum voltage at which a tremor suppression or side effects occurred). Additionally, we compared the choice of the effective contact between T1 and T2 which might be affected by a surgical induced "brain shift." Discussion: Over a time span of about 4 years VIM-DBS in ET showed continuous efficacy in tremor suppression during stim-ON compared to stim-OFF. Compared to immediate postoperative programming sessions in ET-patients with DBS, long-term evaluation showed no relevant change in the choice of contact with respect to side effects and efficacy. In the majority of the cases the active contact at T2 did not correspond to the most effective intraoperative stimulation site T1, which might be explained by a brain-shift due to cerebral spinal fluid loss after neurosurgical procedure.
Keywords: DBS; VIM; brain shift; essential tremor; ventralis intermedius nucleus.
Copyright © 2020 Reitz, Luger, Lapa, Eibach, Filmann, Seifert, Weise, Klein, Kang, Baudrexel and Quick-Weller.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

