Iso-Oncotic Albumin Mitigates Brain and Kidney Injury in Experimental Focal Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 33013661
- PMCID: PMC7494813
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.01001
Iso-Oncotic Albumin Mitigates Brain and Kidney Injury in Experimental Focal Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
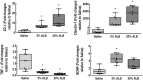
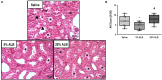
Background: There is widespread debate regarding the use of albumin in ischemic stroke. We tested the hypothesis that an iso-oncotic solution of albumin (5%), administered earlier after acute ischemic stroke (3 h), could provide neuroprotection without causing kidney damage, compared to a hyper-oncotic albumin (20%) and saline. Objective: To compare the effects of saline, iso-oncotic albumin, and hyper-oncotic albumin, all titrated to similar hemodynamic targets, on the brain and kidney. Methods: Ischemic stroke was induced in anesthetized male Wistar rats (n = 30; weight 437 ± 68 g) by thermocoagulation of pial blood vessels of the primary somatosensory, motor, and sensorimotor cortices. After 3 h, animals were anesthetized and randomly assigned (n = 8) to receive 0.9% NaCl (Saline), iso-oncotic albumin (5% ALB), and hyper-oncotic albumin (20% ALB), aiming to maintain hemodynamic stability (defined as distensibility index of inferior vena cava <25%, mean arterial pressure >80 mmHg). Rats were then ventilated using protective strategies for 2 h. Of these 30 animals, 6 were used as controls (focal ischemic stroke/no fluid). Results: The total fluid volume infused was higher in the Saline group than in the 5% ALB and 20% ALB groups (mean ± SD, 4.3 ± 1.6 vs. 2.7 ± 0.6 and 2.6 ± 0.5 mL, p = 0.03 and p = 0.02, respectively). The total albumin volume infused (g/kg) was higher in the 20% ALB group than in the 5% ALB group (1.4 ± 0.6 vs. 0.4 ± 0.2, p < 0.001). Saline increased neurodegeneration (Fluoro-Jade C staining), brain inflammation in the penumbra (higher tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression), and blood-brain barrier damage (lower gene expressions of claudin-1 and zona occludens-1) compared to both iso-oncotic and hyper-oncotic albumins, whereas it reduced the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (a marker of neuroregeneration) compared only to iso-oncotic albumin. In the kidney, hyper-oncotic albumin led to greater damage as well as higher gene expressions of kidney injury molecule-1 and interleukin-6 than 5% ALB (p < 0.001). Conclusions: In this model of focal ischemic stroke, only iso-oncotic albumin had a protective effect against brain and kidney damage. Fluid therapy thus requires careful analysis of impact not only on the brain but also on the kidney.
Keywords: albumin; hemodynamic; inflammation; kidney damage; stroke.
Copyright © 2020 Mendes, Martins, Oliveira, Rocha, Cruz, Antunes, Abreu, Silva, Takiya, Pimentel-Coelho, Robba, Mendez-Otero, Pelosi, Rocco and Silva.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of crystalloid, hyper-oncotic albumin, and iso-oncotic albumin on lung and kidney damage in experimental acute lung injury.Respir Res. 2019 Jul 16;20(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1115-x. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31311539 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of oncotic pressure of diaspirin cross-linked hemoglobin (DCLHb) on brain injury after temporary focal cerebral ischemia in rats.Anesth Analg. 1996 Aug;83(2):342-7. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199608000-00024. Anesth Analg. 1996. PMID: 8694316
-
Long-term high-colloid oncotic therapy for ischemic brain edema in gerbils.Stroke. 1995 Nov;26(11):2149-53. doi: 10.1161/01.str.26.11.2149. Stroke. 1995. PMID: 7482664
-
Docosahexaenoic acid complexed to human albumin in experimental stroke: neuroprotective efficacy with a wide therapeutic window.Exp Transl Stroke Med. 2012 Sep 14;4(1):19. doi: 10.1186/2040-7378-4-19. Exp Transl Stroke Med. 2012. PMID: 22980673 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Albumin Levels: A Biomarker to Be Repurposed in Different Disease Settings in Clinical Practice.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 17;12(18):6017. doi: 10.3390/jcm12186017. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37762957 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of different sodium concentrations in fluids on brain, lung, and kidney in experimental ischemic stroke.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 21;15(1):26496. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12491-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40691260 Free PMC article.
-
Pressure-support compared with pressure-controlled ventilation mitigates lung and brain injury in experimental acute ischemic stroke in rats.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2023 Dec 15;11(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s40635-023-00580-w. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2023. PMID: 38102452 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) as a potential predictor and intervention target for perioperative ischemic stroke: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Aug 10;23(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02216-8. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37563630 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effects of dexmedetomidine and propofol on brain and lung damage in experimental acute ischemic stroke.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 30;11(1):23133. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02608-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34848804 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the impact of bisphenol a exposure on gene expression and immune response in diabetic nephropathy through integrative toxicogenomics and molecular dynamics approaches.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Aug 18;17(1):340. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01874-7. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40826470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker KJ, et al. . 2018 Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart association/American stroke association. Stroke. (2018) 49:e46–110. 10.1161/STR.0000000000000172 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

