Detection of Tn 7-Like Transposons and Antibiotic Resistance in Enterobacterales From Animals Used for Food Production With Identification of Three Novel Transposons Tn 6813, Tn 6814, and Tn 6765
- PMID: 33013752
- PMCID: PMC7500258
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.02049
Detection of Tn 7-Like Transposons and Antibiotic Resistance in Enterobacterales From Animals Used for Food Production With Identification of Three Novel Transposons Tn 6813, Tn 6814, and Tn 6765
Abstract
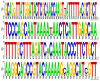
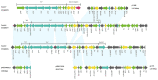
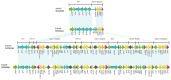
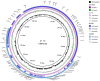
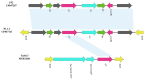
Enterobacterales are widely distributed in the gastro-intestinal system of animals and may cause opportunistic infections. Worse still, multidrug-resistant Enterobacterales also poses a serious threat to public health. Tn7-like transposons have been found in several species of the Enterobacterales order and play an important role in dissemination of antibiotic resistance. This study aimed to investigate the distribution and genetic characterization of Tn7-like transposons in Enterobacterales isolates from food animals and their association with antibiotic resistance. Enterobacterales isolated from the samples were identified and classified according to the 16S rDNA sequence. Tn7-like transposons and associated integrons were detected by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequencing. The antibiotic resistance of each Tn7-like transposon positive isolate was detected according to the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method. Then, six representative strains were selected to study the genetic environment by whole-genome sequencing (WGS). In total, we isolated 377 Tn7-like transposons positive strains of Enterobacterales. Class 2 integrons were detected in 99.5% of the isolates, and there were high frequency mutation sites especially in base 535, a stop mutation. Many isolates (54.9%) were multidrug-resistant and observed high resistance rates to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and streptomycin. Among these strains, we found three new types of Tn7-like transposons, named Tn6813, Tn6814, and Tn6765. This is the first comprehensive survey that shows Tn7-like transposons in Enterobacterales from animals used for food production in different regions of China. This study also provides an insight into the horizontal transfer of resistance genes associated with Tn7-like transposons.
Keywords: Enterobacterales; Tn7-like transposons; animals used for food production; antibiotic resistance; class 2 integrons.
Copyright © 2020 He, Li, Cui and Wang.
Figures
References
-
- Beutlich J., Jahn S., Malorny B., Hauser E., Huhn S., Schroeter A., et al. . (2011). Antimicrobial resistance and virulence determinants in European Salmonella genomic island 1-positive Salmonella enterica isolates from different origins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 5655–5664. 10.1128/AEM.00425-11, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Y. P., Lei C. W., Kong L. H., Zeng J. X., Zhang X. Z., Liu B. H., et al. . (2018). Tn6450, a novel multidrug resistance transposon characterized in a Proteus mirabilis isolate from chicken in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62, e02192–e02217. 10.1128/AAC.02192-17, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

