Biased MAIT TCR Usage Poised for Limited Antigen Diversity?
- PMID: 33013835
- PMCID: PMC7461848
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01845
Biased MAIT TCR Usage Poised for Limited Antigen Diversity?
Abstract
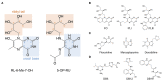
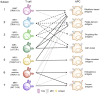
Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are a subset of unconventional T cells that recognize the evolutionarily conserved major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-like antigen-presenting molecule known as MHC class I related protein 1 (MR1). Since their rise from obscurity in the early 1990s, the study of MAIT cells has grown substantially, accelerating our fundamental understanding of these cells and their possible roles in immunity. In the context of recent advances, we review here the relationship between MR1, antigen, and TCR usage among MAIT and other MR1-reactive T cells and provide a speculative discussion.
Keywords: MAIT cells; MR1; T cell subsets; TCR repertoire diversity; antigen diversity.
Copyright © 2020 Souter and Eckle.
Figures

References
-
- Porcelli S, Yockey CE, Brenner MB, Balk SP. Analysis of T cell antigen receptor (TCR) expression by human peripheral blood CD4-8- alpha/beta T cells demonstrates preferential use of several V beta genes and an invariant TCR alpha chain. J Exp Med. (1993) 178:1–16. 10.1084/jem.178.1.1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tilloy F, Treiner E, Park SH, Garcia C, Lemonnier F, De La Salle H, et al. An invariant T cell receptor alpha chain defines a novel TAP-independent major histocompatibility complex class Ib-restricted alpha/beta T cell subpopulation in mammals. J Exp Med. (1999) 189:1907–21. 10.1084/jem.189.12.1907 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

