Prediction of Radiosensitivity in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Based on Multiple Omics Data
- PMID: 33014019
- PMCID: PMC7461877
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00960
Prediction of Radiosensitivity in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Based on Multiple Omics Data
Abstract
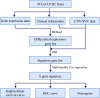
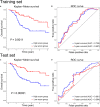
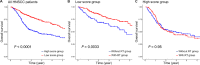
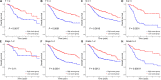
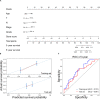
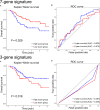
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a malignant tumor. Radiotherapy (RT) is an important treatment for HNSCC, but not all patients derive survival benefit from RT due to the individual differences on radiosensitivity. A prediction model of radiosensitivity based on multiple omics data might solve this problem. Compared with single omics data, multiple omics data can illuminate more systematical associations between complex molecular characteristics and cancer phenotypes. In this study, we obtained 122 differential expression genes by analyzing the gene expression data of HNSCC patients with RT (N = 287) and without RT (N = 189) downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas. Then, HNSCC patients with RT were randomly divided into a training set (N = 149) and a test set (N = 138). Finally, we combined multiple omics data of 122 differential genes with clinical outcomes on the training set to establish a 12-gene signature by two-stage regularization and multivariable Cox regression models. Using the median score of the 12-gene signature on the training set as the cutoff value, the patients were divided into the high- and low-score groups. The analysis revealed that patients in the low-score group had higher radiosensitivity and would benefit from RT. Furthermore, we developed a nomogram to predict the overall survival of HNSCC patients with RT. We compared the prognostic value of 12-gene signature with those of the gene signatures based on single omics data. It suggested that the 12-gene signature based on multiple omics data achieved the best ability for predicting radiosensitivity. In conclusion, the proposed 12-gene signature is a promising biomarker for estimating the RT options in HNSCC patients.
Keywords: gene signature; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; multiple omics data; radiosensitivity; radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2020 Liu, Han, Yue, Dong, Wen, Zhao, Wu, Xia and Bin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prediction of radiotherapy response with a 5-microRNA signature-based nomogram in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2018 Mar;7(3):726-735. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1369. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 29473326 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Radiosensitivity Gene Signature and PD-L1 Status Predicts Clinical Outcome of Patients With Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Study Based on The Cancer Genome Atlas Dataset.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Dec 14;8:775562. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.775562. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34970597 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of 4-lncRNA prognostic signature in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Jun;120(6):10010-10020. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28284. Epub 2018 Dec 11. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30548328
-
Transcriptomics and Epigenomics in head and neck cancer: available repositories and molecular signatures.Cancers Head Neck. 2020 Jan 21;5:2. doi: 10.1186/s41199-020-0047-y. eCollection 2020. Cancers Head Neck. 2020. PMID: 31988797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Biomarkers of Tumour Radiosensitivity and Predicting Benefit from Radiotherapy: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 20;16(10):1942. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101942. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38792019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MRI-based radiomic prognostic signature for locally advanced oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: development, testing and comparison with genomic prognostic signatures.Biomark Res. 2023 Jul 16;11(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s40364-023-00494-5. Biomark Res. 2023. PMID: 37455307 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a prediction model for radiotherapy response among patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on the tumor immune microenvironment and hypoxia signature.Cancer Med. 2022 Dec;11(23):4673-4687. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4791. Epub 2022 May 3. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35505641 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of radiosensitivity and radiocurability using a novel supervised artificial neural network.BMC Cancer. 2022 Dec 1;22(1):1243. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10339-3. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36451111 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting radiotherapy efficacy and prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma through an in-depth analysis of a radiosensitivity gene signature.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 26;14:1334747. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1334747. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39252950 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation Response in the Tumour Microenvironment: Predictive Biomarkers and Future Perspectives.J Pers Med. 2021 Jan 16;11(1):53. doi: 10.3390/jpm11010053. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33467153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- David C. R. (1972). Regression models and life tables. J. R. Stat. Soc. B. 34 187–220.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

