Standardized Surgical Management for Cystic Dilation of the Bile Ducts Based on Clinical and Pathological Studies: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 33014038
- PMCID: PMC7512076
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3432786
Standardized Surgical Management for Cystic Dilation of the Bile Ducts Based on Clinical and Pathological Studies: A Narrative Review
Abstract
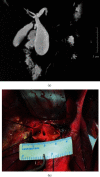
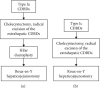
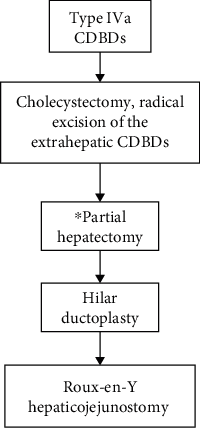
The surgical method of complete/radical cyst excision plus Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy remains the primary therapy and the only effective treatment for cystic dilation of the bile ducts (CDBDs). However, the incidence of long-term postoperative complications is still high, as is the reoperation rate, and the potential for postoperative malignant transformation still exists. In recent years, significant progress has been made in understanding the pathogenic mechanism and pathological changes of adult CDBDs. Based on which, the surgical procedures for CDBDs have been revised to further improve their effectiveness. The purpose of this review is to systematically summarize the latest concepts of the etiology and pathogenic mechanism and the pathological changes of adult CDBDs. Based on the findings of these clinical and pathological studies, a comprehensive theoretical system in the surgical treatment of CDBDs has been established, which corrects many previous theoretical misunderstandings. The specific surgical method for each type of CDBDs and the key technical notes are also described in detail. Using these principles, treatment outcomes for CDBDs can be significantly improved, and the current high complication rate, reoperation rate, and rate of postoperative malignant transformation can be reduced.
Copyright © 2020 Hong-Tian Xia.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
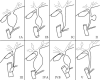
- Todani T., Watanabe Y., Narusue M., Tabuchi K., Okajima K. Congenital bile duct cysts. Classification, operative procedures, and review of thirty-seven cases including cancer arising from choledochal cyst. American Journal of Surgery. 1977;134(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(77)90359-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

