Effect of Aqueous Extract of Adansonia digitata Stem Bark on the Development of Hypertension in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rat Model
- PMID: 33014103
- PMCID: PMC7519996
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3678469
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Adansonia digitata Stem Bark on the Development of Hypertension in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rat Model
Abstract
Background: Adansonia digitata is a plant used against cardiovascular disorders in African folk medicine. We assessed the effects of the aqueous extract of its stem bark on the development of hypertension in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats.
Methods: The animals were administered L-NAME once daily for 3 weeks (25 mg/kg, i.p.), concomitantly with aqueous extract of A. digitata stem bark (100 and 200 mg/kg, p.o.) or captopril (20 mg/kg, p.o.). Then, hemodynamic and electrocardiographic parameters, oxidative stress markers, and the lipid profile were assessed in the blood and heart, aorta, and kidney homogenates, and histopathological analyses were performed.
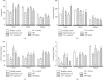
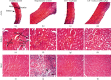
Results: L-NAME-induced hypertensive control animals, but not the animals concomitantly treated with A. digitata extract, displayed increases in the mean arterial blood pressure (21.64% difference, p < 0.001, vs. dose 200 mg/kg), systolic arterial blood pressure (21.33%, p < 0.001), and the diastolic arterial blood pressure (21.84%, p < 0.001). In addition, hypertensive control animals displayed (i) increases in serum triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL, and creatinine levels, malondialdehyde and transaminase activities, and atherogenic index; (ii) decreases in serum HDL, catalase, reduced glutathione, and nitric oxide; and (iii) aorta wall thickening, inflammatory cell infiltration, and cell loss in the cardiac muscle and renal tissues. As captopril, the extract prevented hypertension-like changes in lipid profile, cardiac, hepatic, and renal affection indicators, and oxidative stress markers.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that the extract of A. digitata has antihypertensive and antioxidant effects in L-NAME-induced hypertension rat models. These effects partly justify the traditional medicine use against cardiovascular disorders.
Copyright © 2020 Fidèle Ntchapda et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antihypertensive Effects of the Vitex cienkowskii (Verbenaceae) Stem-Bark Extract on L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Mar 5;2021:6668919. doi: 10.1155/2021/6668919. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33747111 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and chronic antihypertensive effects of Cinnamomum zeylanicum stem bark methanol extract in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Jan 31;13:27. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-27. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013. PMID: 23368533 Free PMC article.
-
Antihypertensive and antioxidant effects of Allanblackia floribunda Oliv. (Clusiaceae) aqueous extract in alcohol- and sucrose-induced hypertensive rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Apr 21;128(3):634-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.02.025. Epub 2010 Mar 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20193752
-
Effect of Methanol Extract of Baobab (Adansonia digitata L.) Fruit Pulp on NG-Nitro-L-Arginine Methyl Ester (L-NAME) Induced Hypertension in Rats.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021 May;28(3):291-300. doi: 10.1007/s40292-021-00448-8. Epub 2021 Apr 7. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021. PMID: 33826116
-
Antioxidant and vasorelaxant effects of aqueous extract of large cardamom in L-NAME induced hypertensive rats.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2020 Oct 2;42(7):581-589. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2020.1739699. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32202168
Cited by
-
The Potential Uses of Baobab Tree's Medicinal Effects in Dentistry: A Literature Review.Cureus. 2023 Nov 23;15(11):e49304. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49304. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38957190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Toxicity and Hypotensive Influence of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Yellow Silk Cocoons of Bombyx mori in Rodent Studies.Foods. 2024 Nov 1;13(21):3505. doi: 10.3390/foods13213505. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39517289 Free PMC article.
-
Ajuga bracteosa Exerts Antihypertensive Activity in l-NAME-Induced Hypertension Possibly through Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Proinflammatory Cytokines, and the Nitric Oxide/Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate Pathway.ACS Omega. 2022 Sep 8;7(37):33307-33319. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03888. eCollection 2022 Sep 20. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36157749 Free PMC article.
-
Antihypertensive Effects of the Vitex cienkowskii (Verbenaceae) Stem-Bark Extract on L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Mar 5;2021:6668919. doi: 10.1155/2021/6668919. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33747111 Free PMC article.
-
Explication of Pharmacological Proficiency of Phytoconstituents from Adansonia digitata Bark: An In Vitro and In Silico Approaches.Scientifica (Cairo). 2024 Aug 16;2024:6645824. doi: 10.1155/2024/6645824. eCollection 2024. Scientifica (Cairo). 2024. PMID: 39184813 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials