Effect of Moxibustion on the Serum Levels of MMP-1, MMP-3, and VEGF in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 33014110
- PMCID: PMC7519456
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7150605
Effect of Moxibustion on the Serum Levels of MMP-1, MMP-3, and VEGF in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease, which will eventually lead to joints deformity and functional damage. The aim of this research is to evaluate the effect of moxibustion on the serum indicators related to bone and cartilage metabolism, matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1), matrix metalloproteinase 3 (MMP-3), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in patients with RA and to explore the mechanism of moxibustion in the treatment of RA.
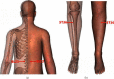
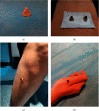
Methods: We recruited 70 RA patients who met the inclusion criteria, and they were randomly divided into two groups, a treatment group and a control group in equal ratio. The control group took methotrexate, folate, or leflunomide orally, while the treatment group received methotrexate, folate, or leflunomide orally and moxibustion at ST36 (Zusanli), BL23 (Shen shu), and Ashi points. We compared the clinical symptoms, RA serological disease markers and serum contents of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), MMP-1, MMP-3, and VEGF of RA patients before and after treatment.
Results: (1) The clinical symptoms and RA serological disease markers of the two groups improved after treatment (P < 0.05), while the clinical symptoms of the treatment group were significantly improved in comparison with the control group (P < 0.05). (2) The levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and VEGF decreased in both groups after treatment (P < 0.05), but the treatment group was significantly decreased compared with the control group (P < 0.05). (3) There were significant differences in MMP-1 and MMP-3 contents after treatment in the treatment group (P < 0.05, P < 0.05), while there were no significant differences in the control group (P > 0.05, P > 0.05). Above all, the contents of IL-1β, TNF-α, MMP-1, MMP-3, and VEGF in the treatment group decreased more significantly than those in the control group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The improvement effect of moxibustion on the clinical symptoms of RA patients may be related to influence on the contents of IL-1β, TNF-α, MMP-1, MMP-3, and VEGF, and moxibustion may play a potential role in bone protection.
Copyright © 2020 Zeyun Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

