Diagnostic accuracy of the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score for the prediction of undiagnosed type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, and metabolic syndrome in the Lebanese University
- PMID: 33014142
- PMCID: PMC7526372
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-020-00590-8
Diagnostic accuracy of the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score for the prediction of undiagnosed type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, and metabolic syndrome in the Lebanese University
Abstract
Background: Risk scores were mainly proved to predict undiagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (UT2DM) in a non-invasive manner and to guide earlier clinical treatment. The objective of the present study was to assess the performance of the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score (FINDRISC) for detecting three outcomes: UT2DM, prediabetes, and the metabolic syndrome (MS).
Methods: This was a prospective, cross-sectional study during which employees aged between 30 and 64, with no known diabetes and working within the faculties of the Lebanese University (LU) were conveniently recruited. Participants completed the FINDRISC questionnaire and their glucose levels were examined using both fasting blood glucose (FBG) and oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT). Furthermore, they underwent lipid profile tests with anthropometry.
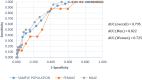
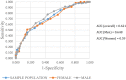
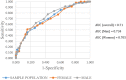
Results: Of 713 subjects, 397 subjects (55.2% female; 44.8% male) completed the blood tests and thus were considered as the sample population. 7.6% had UT2DM, 22.9% prediabetes and 35.8% had MS, where men had higher prevalence than women for these 3 outcomes (P = 0.001, P = 0.003 and P = 0.001) respectively. The AUROC value with 95% Confidence Interval (CI) for detecting UT2DM was 0.795 (0.822 in men and 0.725 in women), 0.621(0.648 in men and 0.59 in women) for prediabetes and 0.710 (0.734 in men and 0.705 in women) for MS. The correspondent optimal cut-off point for UT2DM was 11.5 (sensitivity = 83.3% and specificity = 61.3%), 9.5 for prediabetes (sensitivity = 73.6% and specificity = 43.1%) and 10.5 (sensitivity = 69.7%; specificity = 56.5%) for MS.
Conclusion: The FINDRISC can be considered a simple, quick, inexpensive, and non-invasive instrument to use in a Lebanese community of working people who are unaware of their health status and who usually report being extremely busy because of their daily hectic work for the screening of UT2DM and MS. However, it poorly screens for prediabetes in this context.
Keywords: AUROC; Cutoff; FBG; FINDRISC; MS; OGTT; Prediabetes; Screening; UT2DM; WC.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Goyal R, Jialal I. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report. U.S. Dept of Health and Human Services; 2017 p. 20.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous