Assessing cognitive load in adolescent and adult students using photoplethysmogram morphometrics
- PMID: 33014183
- PMCID: PMC7501395
- DOI: 10.1007/s11571-020-09617-2
Assessing cognitive load in adolescent and adult students using photoplethysmogram morphometrics
Abstract
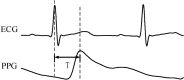
Compared to cardiac parameters and skin conductivities, the photoplethysmogram (PPG) recorded at fingertips and other parts near to peripheral nerve ends have been recently revealed to be yet another sensitive measure for cognitive load assessment. However, there is so far no research on measuring adolescents' cognitive load using physiological signals. A comprehensive study on the effects of PPG morphometrics over a cohort covering both adolescent and adult students is also absent. In this study, we analyze the morphological features of PPG on cognitive load assessment and compare them between adolescent and adult students. Experiments on two-level arithmetic tasks show that the PPG morphometrics reached the same level of significance on the effect of task difficulty/period as heart rate, and different morphological behaviors were also shown between adolescent and adult students during the cognitive task effects, which may imply their physiological differences across age. Physiological signals recorded by wearable devices are also found to be effective in measuring cognitive load.
Keywords: Adolescent cognitive load; Autonomic nervous system; Cognitive load; Heart rate; Photoplethysmogram morphometrics; Wearable devices.
© Springer Nature B.V. 2020.
Figures




References
-
- Askew S. Transforming learning. London: Continuum; 1998.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

