[Gayet-Wernicke encephalopathy: clinical features and radiological anomalies]
- PMID: 33014255
- PMCID: PMC7519788
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2020.36.259.14410
[Gayet-Wernicke encephalopathy: clinical features and radiological anomalies]
Abstract
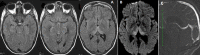
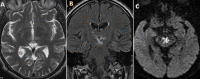
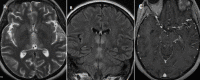
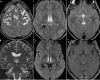
Gayet Wernicke encephalopathy (EGW) is a neurological emergency secondary to thiamine deficiency (vitamin B1). This is more often secondary to chronic alcoholism. The purpose of this study is to remind clinicians of some clinical signs different from ethylism, suggesting EGW as well as to report four cases characterized by different types of anomalies shown by MRI. The average age of patients was 40 years (2 females 2 males). The neurological picture was characterized by disorders of vigilance in all patients, oculomotor disorders in 2 cases, and cerebellar ataxia in one patient. Chronic vomiting was reported in two cases, prolonged fasting in the first case and alcoholism in the second case. MRI of the brain showed anomalies suggesting EGW in all patients with contrast enhancement in one case. Thiamin deficiency was confirmed in two patients. In our context EGW seems to be more frequent in pathological circumstances other than chronic alcoholism (chronic vomiting, severe malnutrition, severe starvation, and chemotherapy...). The clinical signs can suggest other pathologies such as cerebral venous thrombosis, stroke, or other metabolic disorders but MRI excluded them and allowed the diagnosis of EGW. MRI of the brain has an essential role in the diagnosis of EGW. Absence or delay in treatment may influence the prognosis.
L´encéphalopathie de Gayet Wernicke (EGW) est une urgence neurologique secondaire à une carence en thiamine (vitamine B1) le plus souvent secondaire à l´alcoolisme chronique. L´objectif de ce travail est de rappeler certaines situations cliniques évocatrices d´EGW autre que l´éthylisme et les différentes anomalies en IRM autour de 4 observations. L´âge moyen des patients était de 40 ans (2 femmes et 2 hommes). Le tableau neurologique comportait des troubles de la vigilance chez tous les patients, des troubles oculomoteurs dans 2 cas, et une ataxie cérébelleuse chez un seul patient. La notion de vomissements chroniques était notée dans 2 cas, un jeûne prolongé dans un cas et l´alcoolisme pour le dernier. L´IRM cérébrale avait révélé des anomalies évocatrices d´EGW chez tous les patients avec une prise de contraste pour un cas. Le déficit en thiamine était confirmé chez 2 patients. Dans notre contexte l´EGW semble être plus fréquente dans d´autres circonstances pathologiques autres que l´alcoolisme chronique (vomissements chroniques, dénutrition sévère, un jeûne pathologique, et chimiothérapie...). Le contexte clinique peut faire suspecter d´autres pathologies comme la thrombose veineuse cérébrale, l´accident vasculaire cérébral, ou un autre trouble métabolique mais l´IRM a permis de les écarter et de poser le diagnostic d´EGW. L´IRM cérébrale présente un intérêt primordial dans le diagnostic de l´EGW. L´absence ou le retard de la mise en route du traitement influence le pronostic.
Keywords: Gayet Wernicke encephalopathy; MRI anomalies; clinical; context.
Copyright: Siham Bouchal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Les auteurs ne déclarent aucun conflit d´intérêts.
Figures
References
-
- Lenz V, Vargas MI, Bin JF, Bogorin A, Grebici-Bessoum M, Jacques C, Marin H, Zollner G, Dietemann L. Apport de l´IRM dans l´exploration de l´encéphalopathie de Gayet Wernicke. Journal of Neuroradiology. 2002;29(3):153–160. - PubMed
-
- Allan Thomson D, Christopher Cook CH, Irene Guerrini, Donna Sheedy, Clive Harper, Jane Marshall E. Wernicke´s encephalopathy: “plus ça change, plus c´est la même chose”. Alcohol and Alcohol. 2008;43(2):180–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
