Investigation of the Role of Oxidative Stress and Factors Associated with Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy in Patients after Heart Transplantation
- PMID: 33014277
- PMCID: PMC7519194
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7436982
Investigation of the Role of Oxidative Stress and Factors Associated with Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy in Patients after Heart Transplantation
Abstract
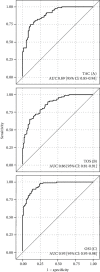
Oxidative stress is defined as an imbalance between the production of free radicals and their elimination by the antioxidant defense system. However, the role of oxidative stress in cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) has not been fully understood. Therefore, this study is aimed at determining the role of oxidative-antioxidative balance disturbances in patients after HT. Furthermore, we sought to analyze factors associated with the presence of CAV, with particular emphasis placed on oxidative stress markers. The study analyzed data of 194 consecutive patients after HT who underwent routine visits in the Transplantation Clinic between 2015 and 2016. Total oxidant status (TOS) and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) were measured by the method described by Erel. The oxidative stress index (OSI) was defined as the ratio of the TOS to TAC levels. Patients' mean age was 55.4 ± 15.0 years, and 73.4% were men. The frequency of CAV was 50%. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curves indicated a good discriminatory power of TAC and TOS (0.8940 (0.8515-0.9365); 0.8620 (0.8126-0.9114), respectively) as well as excellent discriminatory power of OSI (0.9530 (0.9279-0.9781)) for CAV detection. Multivariate analysis of the Cox proportional hazard model confirmed that OSI (hazard ratio (HR) = 1.294 (1.204-1.391), p < 0.0001), age (HR = 1.023 (1.006-1.041), p = 0.0091), and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (HR = 1.049 (1.016-1.083), p = 0.0151) were independently associated with CAV presence. In conclusion, TAC and TOS had a good discriminatory power and OSI had excellent strength for detecting CAV. The independent factors of CAV were higher OSI and CRP levels, as well as older recipient age.
Copyright © 2020 Wioletta Szczurek et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lund L. H., Edwards L. B., Kucheryavaya A. Y., et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirtieth official adult heart transplant report-2013; focus theme: age. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2013;32(10):951–964. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2013.08.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mehra M. R., Crespo-Leiro M. G., Dipchand A., et al. International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation working formulation of a standardized nomenclature for cardiac allograft vasculopathy–2010. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2010;29(7):717–727. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2010.05.017. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous