Metastatic status of sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer determined with photoacoustic microscopy via dual-targeting nanoparticles
- PMID: 33014359
- PMCID: PMC7494891
- DOI: 10.1038/s41377-020-00399-0
Metastatic status of sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer determined with photoacoustic microscopy via dual-targeting nanoparticles
Abstract
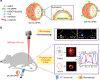
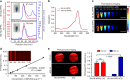
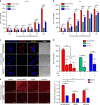
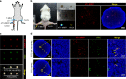
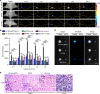
Detection of sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) is critical to guide the treatment of breast cancer. However, distinguishing metastatic SLNs from normal and inflamed lymph nodes (LNs) during surgical resection remains a challenge. Here, we report a CD44 and scavenger receptor class B1 dual-targeting hyaluronic acid nanoparticle (5K-HA-HPPS) loaded with the near-infra-red fluorescent dye DiR-BOA for SLN imaging in breast cancer. The small sized (~40 nm) self-assembled 5K-HA-HPPSs accumulated rapidly in the SLNs after intradermal injection. Compared with normal popliteal LNs (N-LN), there were ~3.2-fold and ~2.4-fold increases in fluorescence intensity in tumour metastatic SLNs (T-MLN) and inflamed LNs (Inf-LN), respectively, 6 h after nanoparticle inoculation. More importantly, photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) of 5K-HA-HPPS showed a significantly distinct distribution in T-MLN compared with N-LN and Inf-LN. Signals were mainly distributed at the centre of T-MLN but at the periphery of N-LN and Inf-LN. The ratio of PA intensity (R) at the centre of the LNs compared with that at the periphery was 5.93 ± 0.75 for T-MLNs of the 5K-HA-HPPS group, which was much higher than that for the Inf-LNs (R = 0.2 ± 0.07) and N-LNs (R = 0.45 ± 0.09). These results suggest that 5K-HA-HPPS injection combined with PAM provides a powerful tool for distinguishing metastatic SLNs from pLNs and inflamed LNs, thus guiding the removal of SLNs during breast cancer surgery.
Keywords: Optical materials and structures; Optical techniques.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA: Cancer J. Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Hayes DF. HER2 and breast cancer—a phenomenal success story. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;381:1284–1286. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

