Multicomponent Exercise Training Improves Gait Ability of Older Women Rather than Strength Training: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 33014466
- PMCID: PMC7519190
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6345753
Multicomponent Exercise Training Improves Gait Ability of Older Women Rather than Strength Training: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to compare the effects of multicomponent and strength training programs on dynamic balance, functional capacity, and gait ability in older women.
Methods: Thirty individuals (67 ± 4.3 years; 30.6 ± 3.9 kg/m2) were trained for 12 weeks (3 times per week), following multicomponent (MG: exercises focusing on agility, balance, muscle strength, and aerobic) and strength programs (SG: lower limbs strength exercise).
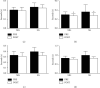
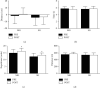
Results: Peak torque of hip flexors (p=0.020) and extensors (p=0.009) and knee flexors (p=0.001) of SG was greater than that of MG at posttraining. In addition, both groups increased peak torque of knee extensors (p=0.002) and plantar extensors with higher effect size for SG (d = -0.41 and -0.48), whereas MG presented higher effect size for plantar flexors muscles (d = -0.55). Only the SG improved the rate of torque development of knee extensors (29%; p=0.002), and this variable was also greater to SG than MG at posttraining (106%). The SG and MG improved dynamic balance although SG presented higher effect size (d = 0.61). Both groups improved the performance on 30 s sit to stand test (p=0.010) with higher effect size for MG (d = -0.54). Only the MG improved the stride length (4%; p=0.011) and gait speed (10%; p=0.024). In addition, the groups improved toe clearance (p=0.035) and heel contact (p=0.010) with higher effect sizes for MG (d = -0.066 and 1.07).
Conclusion: Strength training should be considered to increase muscle function and dynamic balance in older women, whereas multicomponent training should be considered to increase functional capacity and gait ability in this population.
Copyright © 2020 Renata Wolf et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Orr R. Contribution of muscle weakness to postural instability in the elderly. European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. 2010;46:183–220. - PubMed
-
- Nelson M. E., Rejeski W. J., Blair S. N., Duncan P. W., Judge J. O., King A. C. Physical activity and public health in older adults: recommendation from the American college of sports medicine and the American heart association. Circulation. 2007;116 doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.185650. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

