Chondroprotective Effects of Combination Therapy of Acupotomy and Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Knee Osteoarthritis Rabbits via the GSK3β-Cyclin D1-CDK4/CDK6 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33014527
- PMCID: PMC7505269
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2019.1104
Chondroprotective Effects of Combination Therapy of Acupotomy and Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Knee Osteoarthritis Rabbits via the GSK3β-Cyclin D1-CDK4/CDK6 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
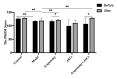
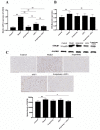
Adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) are highly chondrogenic and can be used to treat knee osteoarthritis (KOA) by alleviating cartilage defects. Acupotomy, a biomechanical therapy guided by traditional Chinese medicine theory, alleviates cartilage degradation and is widely used in the clinic to treat KOA by correcting abnormal mechanics. However, whether combining acupotomy with ASCs will reverse cartilage degeneration by promoting chondrocyte proliferation in KOA rabbits is unknown. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of combination therapy of acupotomy and ASCs on chondrocyte proliferation and to determine the underlying mechanism in rabbits with KOA induced by knee joint immobilization for 6 weeks. After KOA modeling, five groups of rabbits (acupotomy, ASCs, acupotomy + ASCs, model and control groups) received the indicated intervention for 4 weeks. The combination therapy significantly restored the KOA-induced decrease in passive range of motion (PROM) in the knee joint and reduced the elevated serum level of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP), a marker for cartilage degeneration. Furthermore, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images showed that the combination therapy inhibited cartilage injury. The combination therapy also significantly blocked increases in the mRNA and protein expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) and decreases in the mRNA and protein expression of cyclin D1/CDK4 and cyclin D1/CDK6 in cartilage. These findings indicated that the combination therapy mitigated knee joint immobility, promoted chondrocyte proliferation and alleviated cartilage degeneration in KOA rabbits, and these effects may be mediated by specifically regulating the GSK3β-cyclin D1-CDK4/CDK6 pathway.
Keywords: ASCs; KOA; acupotomy; chondrocytes; proliferation.
copyright: © 2020 An et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Acupotomy alleviates knee osteoarthritis in rabbit by regulating chondrocyte mitophagy Pink1-Parkin pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Jun;44(3):468-477. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240402.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38767630 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of acupotomy on chondrocyte ferroptosis in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis based on HSPA5/GPX4 signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2024 May 12;44(5):555-64. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20230901-k0001. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2024. PMID: 38764106 Chinese.
-
[Effect of acupotomy on expressions of cellular senescence markers p16Ink4a and p21Waf1/Cip1 in cartilage tissue of rabbits with knee osteoarthritis].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023 Jul 25;48(7):658-65. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20221091. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 37518959 Chinese.
-
[Research progress of effect mechanism of acupotomy for knee osteoarthritis].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025 Jun 12;45(6):867-874. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20250106-k0003. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40518794 Review. Chinese.
-
Vitamin D and autophagy in knee osteoarthritis: A review.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Oct;123:110712. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110712. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37523972 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness and safety of acupotomy for knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Nov 20;22(1):824. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05786-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34801083 Free PMC article.
-
[Electroacupuncture improves motor function of rats with osteoarthritis by alleviating joint inflammation through the Wnt-7B/β-catenin signaling pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Apr 20;43(4):590-596. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.04.12. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37202195 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Cell-based therapies have disease-modifying effects on osteoarthritis in animal models. A systematic review by the ESSKA Orthobiologic Initiative. Part 1: adipose tissue-derived cell-based injectable therapies.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023 Feb;31(2):641-655. doi: 10.1007/s00167-022-07063-7. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023. PMID: 36104484 Free PMC article.
-
Cartilage regeneration and inflammation modulation in knee osteoarthritis following injection of allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells: a phase II, triple-blinded, placebo controlled, randomized trial.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Jun 14;14(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03359-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37316949 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Acupotomy ameliorates subchondral bone absorption and mechanical properties in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis by regulating bone morphogenetic protein 2-Smad1 pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2023 Aug;43(4):734-743. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230404.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 37454258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glynjones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, Price AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H, et al. (2015). Osteoarthritis. Lancet, 386:376-387. - PubMed
-
- Karsdal MA, Michaelis M, Ladel C, Siebuhr AS, Bihlet AR, Andersen JR, et al. (2016). Disease-modifying treatments for osteoarthritis (DMOADs) of the knee and hip: lessons learned from failures and opportunities for the future. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 24:2013-2021. - PubMed
-
- Aigner T, Kim HA, Roach HI (2004). Apoptosis in osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am, 30:639-653. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto T, Cooper GM, Gharaibeh B, Meszaros LB, Li G, Usas A, et al. (2009). Cartilage repair in a rat model of osteoarthritis through intraarticular transplantation of muscle-derived stem cells expressing bone morphogenetic protein 4 and soluble Flt-1. Arthritis Rheum, 60:1390-1405. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
