Stem Cell Based Therapy Option in COVID-19: Is It Really Promising?
- PMID: 33014531
- PMCID: PMC7505270
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2020.0608
Stem Cell Based Therapy Option in COVID-19: Is It Really Promising?
Abstract
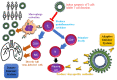
The COVID-19 patients were first detected in China, in December 2019, then the novel virus with associated pneumonia and other diseases spread quickly to worldwide becoming a serious public health intimidation. Despite all the efforts, the pharmacological agents used for controlling or treating the disease, especially respiratory problems, have not been accomplished so far. Among various treatment options, mesenchymal stem cell-based cellular therapies are being investigated, because of their regeneration ability and multipotency along with other features like immunomodulation, antifibrosis and anti-inflammatory effects. This paper intends to analyze the current clinical trials on stem cell treatment of novel virus, searching and reviewing the available information and the International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) of World Health Organization (WHO). We concluded that the stem cell treatment of COVID-19 is found promising with pilot studies' results, but still in the early development phase. There is an urgent need for large-scale investigations to confirm and validate the safety and efficacy profile of these therapies with reliable scientific evidence.
Keywords: COVID-19; Stem cell; clinical; treatment; trials.
copyright: © 2020 Irmak et al.
Figures

References
-
- Demircan PC, Sariboyacı AE, Unal ZS, Gacar G, Subasi C, Karaoz E (2011). Immunoregulatory effects of human dental pulp-derived stem cells on T cells: comparison of transwell co-culture and mixed lymphocyte reaction systems. Cytotherapy, 13:1205-20. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
