Adaptive shrinking reconstruction framework for cone-beam X-ray luminescence computed tomography
- PMID: 33014562
- PMCID: PMC7510911
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.393970
Adaptive shrinking reconstruction framework for cone-beam X-ray luminescence computed tomography
Abstract
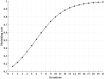
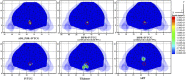
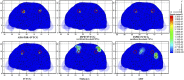
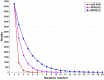
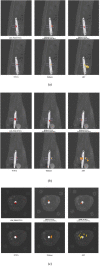
Cone-beam X-ray luminescence computed tomography (CB-XLCT) emerged as a novel hybrid technique for early detection of small tumors in vivo. However, severe ill-posedness is still a challenge for CB-XLCT imaging. In this study, an adaptive shrinking reconstruction framework without a prior information is proposed for CB-XLCT. In reconstruction processing, the mesh nodes are automatically selected with higher probability to contribute to the distribution of target for imaging. Specially, an adaptive shrinking function is designed to automatically control the permissible source region at a multi-scale rate. Both 3D digital mouse and in vivo experiments were carried out to test the performance of our method. The results indicate that the proposed framework can dramatically improve the imaging quality of CB-XLCT.
© 2020 Optical Society of America under the terms of the OSA Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ahmad M., Pratx G., Bazalova M., Xing L., “X-ray luminescence and x-ray fluorescence computed tomography: new molecular imaging modalities,” IEEE Access 2(2), 1051–1061 (2014).10.1109/ACCESS.2014.2353041 - DOI
-
- Zhang S., Ma X., Wang Y., Wu M., Meng H., Chai W., Wang X., Wei S., Tian J., “Robust reconstruction of fluorescence molecular tomography based on sparsity adaptive correntropy matching pursuit method for stem cell distribution,” IEEE T. Med. Imaging 37(10), 2176–2184 (2018).10.1109/TMI.2018.2825102 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
