AV-Net: deep learning for fully automated artery-vein classification in optical coherence tomography angiography
- PMID: 33014612
- PMCID: PMC7510886
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.399514
AV-Net: deep learning for fully automated artery-vein classification in optical coherence tomography angiography
Abstract
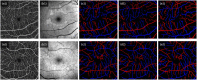
This study is to demonstrate deep learning for automated artery-vein (AV) classification in optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA). The AV-Net, a fully convolutional network (FCN) based on modified U-shaped CNN architecture, incorporates enface OCT and OCTA to differentiate arteries and veins. For the multi-modal training process, the enface OCT works as a near infrared fundus image to provide vessel intensity profiles, and the OCTA contains blood flow strength and vessel geometry features. A transfer learning process is also integrated to compensate for the limitation of available dataset size of OCTA, which is a relatively new imaging modality. By providing an average accuracy of 86.75%, the AV-Net promises a fully automated platform to foster clinical deployment of differential AV analysis in OCTA.
© 2020 Optical Society of America under the terms of the OSA Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interest exists for any author.
Figures

References
-
- Hatanaka Y., Nakagawa T., Aoyama A., Zhou X., Hara T., Fujita H., Kakogawa M., Hayashi Y., Mizukusa Y., Fujita A., “Automated detection algorithm for arteriolar narrowing on fundus images,” in 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, (IEEE, 2006), 286–289. - PubMed
-
- Ikram M. K., Janssen J. A., Roos A. M., Rietveld I., Witteman J. C., Breteler M. M., Hofman A., Van Duijn C. M., de Jong P. T., “Retinal vessel diameters and risk of impaired fasting glucose or diabetes: the Rotterdam study,” Diabetes 55(2), 506–510 (2006).10.2337/diabetes.55.02.06.db05-0546 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
