NF-κB signaling induces inductive expression of the downstream molecules and IgD gene in the freshwater carp, Catla catla
- PMID: 33014688
- PMCID: PMC7502101
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-020-02435-7
NF-κB signaling induces inductive expression of the downstream molecules and IgD gene in the freshwater carp, Catla catla
Abstract
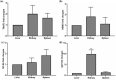
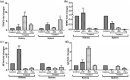
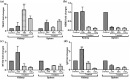
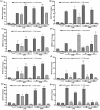
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in innate immune system act as primary sensors in detecting the microbial components and activate their signaling cascades to induce NF-κB (nuclear factor NF-κB) towards the augmentation of immunoglobulin (Ig) synthesis. To gain insights into the efficacy of NF-κB pathway in immunoglobulin D (IgD) synthesis in the Indian Major Carp Catla catla, cloning and sequencing of TLR-signaling downstream molecules [TRAF3 (TNF receptor-associated factor 3), NEMO (nuclear factor-kappa B essential modulator), NF-κB and BAFF (B cell activating factor)] were performed by infecting the fish with pathogens. mRNA expression analysis of the downstream molecules and IgD showed significant up-regulation of these genes in kidney (P ≤ 0.001) as compared to spleen (P ≤ 0.05). To ascertain the role of NF-κB pathway in IgD synthesis, the primary cell culture of kidney and spleen in monolayer cell suspension was treated with NF-κB inhibitor (BAY 11-7082) and down-regulation of BAFF, NEMO, NF-κB, and IgD gene was observed. These results highlight the importance of NF-κB signaling pathway in augmenting the IgD gene expression in the freshwater carp, Catla catla.
Keywords: BAFF; Catla catla; IgD; Immunoglobulin; NEMO; NF-κb; TRAF3.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Banerjee R, Patel B, Basu M, Lenka SS, Paicha M, Samanta M, Das S. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of immunoglobulin D on pathogen challenge and pathogen associated molecular patterns stimulation in freshwater carp, Catla catla. Microbiol Immunol. 2017;61:452–458. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12534. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

