Reciprocal Interplay Between Fibrillar Collagens and Collagen-Binding Integrins: Implications in Cancer Progression and Metastasis
- PMID: 33014790
- PMCID: PMC7461916
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01488
Reciprocal Interplay Between Fibrillar Collagens and Collagen-Binding Integrins: Implications in Cancer Progression and Metastasis
Abstract
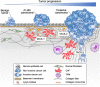
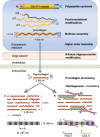
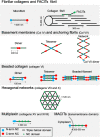
Cancers are complex ecosystems composed of malignant cells embedded in an intricate microenvironment made of different non-transformed cell types and extracellular matrix (ECM) components. The tumor microenvironment is governed by constantly evolving cell-cell and cell-ECM interactions, which are now recognized as key actors in the genesis, progression and treatment of cancer lesions. The ECM is composed of a multitude of fibrous proteins, matricellular-associated proteins, and proteoglycans. This complex structure plays critical roles in cancer progression: it functions as the scaffold for tissues organization and provides biochemical and biomechanical signals that regulate key cancer hallmarks including cell growth, survival, migration, differentiation, angiogenesis, and immune response. Cells sense the biochemical and mechanical properties of the ECM through specialized transmembrane receptors that include integrins, discoidin domain receptors, and syndecans. Advanced stages of several carcinomas are characterized by a desmoplastic reaction characterized by an extensive deposition of fibrillar collagens in the microenvironment. This compact network of fibrillar collagens promotes cancer progression and metastasis, and is associated with low survival rates for cancer patients. In this review, we highlight how fibrillar collagens and their corresponding integrin receptors are modulated during cancer progression. We describe how the deposition and alignment of collagen fibers influence the tumor microenvironment and how fibrillar collagen-binding integrins expressed by cancer and stromal cells critically contribute in cancer hallmarks.
Keywords: cancer; extracellular matrix; fibrillar collagens; integrins; metastasis.
Copyright © 2020 Bourgot, Primac, Louis, Noël and Maquoi.
Figures
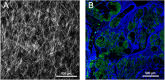
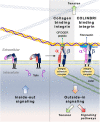
Similar articles
-
Functional Interplay Between Collagen Network and Cell Behavior Within Tumor Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 30;10:527. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00527. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32426274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Breast Cancer.J Clin Med. 2022 Feb 25;11(5):1250. doi: 10.3390/jcm11051250. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35268340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basic Components of Connective Tissues and Extracellular Matrix: Fibronectin, Fibrinogen, Laminin, Elastin, Fibrillins, Fibulins, Matrilins, Tenascins and Thrombospondins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1348:105-126. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-80614-9_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34807416
-
Targeting Tumor-Stromal Interactions in Pancreatic Cancer: Impact of Collagens and Mechanical Traits.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 25;9:787485. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.787485. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34901028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of network-forming collagens in cancer progression.Int J Cancer. 2022 Sep 15;151(6):833-842. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34004. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Int J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35322886 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound-Based Method for the Identification of Novel MicroRNA Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2021 Oct 28;12(11):1726. doi: 10.3390/genes12111726. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34828332 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical Confinement and DDR1 Signaling Synergize to Regulate Collagen-Induced Apoptosis in Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Oct;9(28):e2202552. doi: 10.1002/advs.202202552. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35957513 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling.Open Life Sci. 2023 Sep 19;18(1):20220716. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0716. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37744455 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment signaling and therapeutics in cancer progression.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023 May;43(5):525-561. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12416. Epub 2023 Apr 2. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37005490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of the effects of overexpression of jumping translocation breakpoint (JTB) protein in MCF7 cells for potential use as a biomarker in breast cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Apr 15;12(4):1784-1823. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35530281 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

