Folliculin Controls the Intracellular Survival and Trans-Epithelial Passage of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- PMID: 33014885
- PMCID: PMC7499807
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00422
Folliculin Controls the Intracellular Survival and Trans-Epithelial Passage of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Abstract
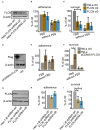
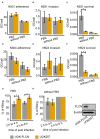
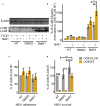
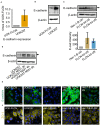
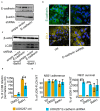
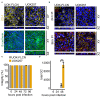
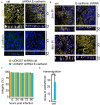
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a Gram-negative obligate human pathogenic bacterium, infects human epithelial cells and causes sexually transmitted diseases. Emerging multi-antibiotic resistant gonococci and increasing numbers of infections complicate the treatment of infected patients. Here, we used an shRNA library screen and next-generation sequencing to identify factors involved in epithelial cell infection. Folliculin (FLCN), a 64 kDa protein with a tumor repressor function was identified as a novel host factor important for N. gonorrhoeae survival after uptake. We further determined that FLCN did not affect N. gonorrhoeae adherence and invasion but was essential for its survival in the cells by modulating autophagy. In addition, FLCN was also required to maintain cell to cell contacts in the epithelial layer. In an infection model with polarized cells, FLCN inhibited the polarized localization of E-cadherin and the transcytosis of gonococci across polarized epithelial cells. In conclusion, we demonstrate here the connection between FLCN and bacterial infection and in particular the role of FLCN in the intracellular survival and transcytosis of gonococci across polarized epithelial cell layers.
Keywords: autophagy; folliculin; gonococcal invasion; polarized cell culture; polarized epithelium.
Copyright © 2020 Yang, Heydarian, Kozjak-Pavlovic, Urban, Harbottle and Rudel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Role of Sphingosine in the Intracellular Survival of Neisseria gonorrhoeae.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 May 12;10:215. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00215. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32477967 Free PMC article.
-
A Subpopulation of Intracellular Neisseria gonorrhoeae Escapes Autophagy-Mediated Killing Inside Epithelial Cells.J Infect Dis. 2019 Jan 1;219(1):133-144. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiy237. J Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 29688440
-
Neisseria gonorrhoeae elicits extracellular traps in primary neutrophil culture while suppressing the oxidative burst.mBio. 2015 Feb 10;6(1):e02452-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02452-14. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25670773 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial Haven and Autophagy Breakout in Gonococci Infection.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 9;8:439. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00439. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32582714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and the Host Defense in Ascending Infections of Human Fallopian Tube.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 21;9:2710. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02710. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30524442 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue Models for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Research-From 2D to 3D.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 11;12:840122. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.840122. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35223556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gonococcal OMV-delivered PorB induces epithelial cell mitophagy.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 23;15(1):1669. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45961-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38396029 Free PMC article.
-
Gonococcal invasion into epithelial cells depends on both cell polarity and ezrin.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Dec 1;17(12):e1009592. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009592. eCollection 2021 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34852011 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

