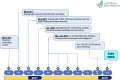
Successful Establishment of the First Neonatal Respiratory Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Program in the Middle East, in Collaboration With Pediatric Services
- PMID: 33014924
- PMCID: PMC7516255
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2020.00506
Successful Establishment of the First Neonatal Respiratory Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Program in the Middle East, in Collaboration With Pediatric Services
Abstract
Background: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is a complex life-saving support for acute cardio-respiratory failure, unresponsive to medical treatment. Starting a new ECMO program requires synergizing different aspects of organizational infrastructures and appropriate extensive training of core team members to deliver the care successfully and safely. Objectives: To describe the process of establishing a new neonatal ECMO program and to evaluate the program by benchmarking the ECMO respiratory outcomes and mechanical complications to the well-established Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO) registry data. Materials and Methods: We reviewed the processes and steps involved in planning and setting up the new ECMO program. To assess the success of the ECMO implementation program, we retrospectively reviewed data of clinical outcomes and technical complications for the first 11 patients who have received ECMO therapy for respiratory indications since program activation (July 2018-May 2020). We analyzed mechanical complications as a tool to measure infrastructures and our effective training for the core team of ECMO specialists. We also looked at all clinical complications and benchmarked these numbers with the last 10 years of ELSO registry data (2009-2019) in the corresponding categories for comparison. Chi-square test was used to compare, and outcomes are presented in percentage; a p-value of <0.05 is considered significant. Results: A total of 27 patients underwent ECMO in the hospital, out of which 11 (six neonatal and five pediatric) patients had acute respiratory failure treated with venovenous (VV) ECMO or veno-arterial (VA) ECMO over a 22-month period. We had a total of 3,360 h of ECMO run with a range from 1 day to 7 weeks on ECMO. Clinical outcomes and mechanical complications are comparable to ELSO registry data (no significant difference); there were no pump failure, oxygenator failure, or pump clots. Conclusions: Establishing the ECMO program involved a multisystem approach with particular attention to the training of ECMO team members. The unified protocols, equipment, and multistep ECMO team training increased staff knowledge, technical skills, and teamwork, allowing the successful development of a neonatal respiratory ECMO program with minimal mechanical complications during ECMO runs, showing a comparable patient flow and mechanical complications.
Keywords: ECMO program; extracorporeal life support; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; meconium aspiration; newborn infant; persistent pulmonary hypertension; respiratory ECMO.
Copyright © 2020 Elkhwad, More, Anand, Al-Maraghi, Crowe, Wong, Metcalf, Yadav and Sigalet.
Figures
References
-
- Goodman A. The development of the Qatar healthcare system: a review of the literature. Int J Clin Med. (2015) 6:177–85. 10.4236/ijcm.2015.63023 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources