A Spellbinding Interplay Between Biological Barcoding and Nanotechnology
- PMID: 33014994
- PMCID: PMC7506030
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00883
A Spellbinding Interplay Between Biological Barcoding and Nanotechnology
Abstract
Great scientific research with improved potential in probing biological locales has remained a giant stride. The use of bio-barcodes with the potential use of nanotechnology is a hallmark being developed among recent advanced techniques. Biobarcoding is a novel method used for screening biomolecules to identify and divulge ragbag biodiversity. It establishes successful barcoding projects in the field of nanomedical technology for massively testing disease diagnosis and treatment. Biobarcoding and nanotechnology are recently developed technologies that provide unique opportunities and challenges for multiplex detection such as DNAs, proteins and nucleic acids of animals, plants, viruses, and various other species. These technologies also clump drug delivery, gene delivery, and DNA sequencing. Bio-barcode amplification assay (BCA) is used at large for the detection and identification of proteins and DNAs. DNA barcoding combined with nanotechnology has been proven highly sensitive rendering fast uniplex and multiplex detection of pathogens in food, blood, and other specimens. This review takes a panoramic view of current advances in nano bio-barcodes which have been summarized to explore additional applications such as detection of cytokines, neurotransmitters, cancer markers, prostate-specific antigens, and allergens. In the future, it will also be possible to detect some fungi, algae, protozoa, and other pollutants in food, agriculture, and clinical samples. Using these technologies, specific and efficient sensors would possibly be developed that can perform swift detections of antigens, allergens, and other specimens.
Keywords: barcoded nanoparticles; biobarcoding; cytokines; nano-barcoding; nano-biosensors; nanotechnology; nucleic acids; proteins.
Copyright © 2020 Munir, Ahmed, Ibrahim, Khalid and Ojha.
Figures
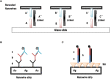




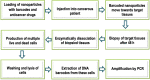
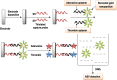


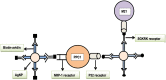
References
-
- Bahadorimehr A., Yunas J., Majlis B. Y. (2010). “Low cost fabrication of microfluidic microchannels for Lab-On-a-Chip applications,” in Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Electronic Devices, Systems and Applications, (Kuala Lumpur: IEEE; ), 242–244.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

