High-Performance Voltammetric Aptasensing Platform for Ultrasensitive Detection of Bisphenol A as an Environmental Pollutant
- PMID: 33015024
- PMCID: PMC7498542
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.574846
High-Performance Voltammetric Aptasensing Platform for Ultrasensitive Detection of Bisphenol A as an Environmental Pollutant
Abstract
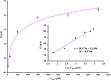
Bisphenol A (BPA) as a pervasive endocrine-disrupting compound (EDC) has been shown to cause multiple detrimental effects including cardiovascular disorders, pregnancy complications, obesity, glucose metabolism disorders, and reproductive toxicity even at a concentration as low as tolerable daily intake (TDI) (4 μg/kg/day). In the present study, a novel ultra-sensitive, electrochemical aptasensor was designed using a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) modified by gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) conjugated to thiolated aptamers for accurate determination of BPA in biological, industrial and environmental samples. To characterize the electrochemical properties of the aptasensor, cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were implemented. Detection of BPA was also performed through differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) in [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- electrolyte solution. Under optimum condition, the present electrochemical aptasensor demonstrated an outstanding linear response in the concentration range of 1 pM to 10 nM with a remarkably low limit of detection of 0.113 pM. Due to the superb affinity between anti-BPA aptamers and BPA molecules, the designed aptasensor did not show any significant interaction with other analytes in real samples. Also, fabricated biosensor remained perfectly stable in long-term storage. The analytical results of the fabricated aptasensor are well compatible with those obtained by the ELISA method, indicating the trustworthiness and reasonable accuracy of the application of aptasensor in real samples. Overall, the proposed aptasensor would be a credible and economical method of precise, reproducible, and highly selective detection of minimum levels of BPA in food containers and clinical samples. This would be a promising strategy to enhance the safety of food products and reduce the risk of BPA daily exposure.
Keywords: bisphenol A; electrochemical aptasensor; endocrine-disrupting compounds; environmental pollutant; toxicology.
Copyright © 2020 Hassani, Rezaei Akmal, Salek Maghsoudi, Rahmani, Vakhshiteh, Norouzi, Ganjali and Abdollahi.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Sensitive Aptamer-Based Biosensor for Electrochemical Quantification of PSA as a Specific Diagnostic Marker of Prostate Cancer.J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2020;23:243-258. doi: 10.18433/jpps31171. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32649855
-
Novel label-free electrochemical aptasensor for determination of Diazinon using gold nanoparticles-modified screen-printed gold electrode.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Nov 30;120:122-128. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.08.041. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 30172234
-
Fabrication of a novel and ultrasensitive label-free electrochemical aptasensor for detection of biomarker prostate specific antigen.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Apr 1;126:1065-1073. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.012. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30611810
-
A microfluidic electrochemical aptasensor for enrichment and detection of bisphenol A.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Oct 15;117:457-463. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.06.036. Epub 2018 Jun 23. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 29982114
-
Fabrication of a novel aptasensor based on three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide/polyaniline/gold nanoparticle composite as a novel platform for high sensitive and specific cocaine detection.Anal Chim Acta. 2017 Dec 15;996:10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.10.035. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Anal Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 29137703
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Nanotechnology-Based Biosensors Development for Detection of Arsenic, Lead, Mercury, and Cadmium.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Feb 4;16:803-832. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S294417. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33568907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI-optimized electrochemical aptasensors for stable, reproducible detection of neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and coronavirus.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 18;11(1):e41338. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41338. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39834418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Fluorescent Aptasensor Based on Assembled G-Quadruplex and Thioflavin T for the Detection of Biomarker VEGF165.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Nov 16;9:764123. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.764123. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34869275 Free PMC article.
-
A Selective Electrochemical Sensor for Bisphenol A Detection Based on Cadmium (II) (bromophenyl)porphyrin and Gold Nanoparticles.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Dec 18;15(12):1508. doi: 10.3390/mi15121508. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770261 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer-Based Lateral Flow Assays: Current Trends in Clinical Diagnostic Rapid Tests.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;15(1):90. doi: 10.3390/ph15010090. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35056148 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abnous K., Danesh N. M., Ramezani M., Alibolandi M., Taghdisi S. M. (2018). A novel electrochemical sensor for bisphenol A detection based on nontarget-induced extension of aptamer length and formation of a physical barrier. Biosens. Bioelectron. 119 204–208. 10.1016/j.bios.2018.08.024 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arduini F., Micheli L., Moscone D., Palleschi G., Piermarini S., Ricci F., et al. (2016). Electrochemical biosensors based on nanomodified screen-printed electrodes: recent applications in clinical analysis TrAC. Trends Analyt. Chem. 79 114–126. 10.1016/j.trac.2016.01.032 - DOI
-
- Baghayeri M., Ansari R., Nodehi M., Razavipanah I., Veisi H. (2018). Label-free electrochemical bisphenol A aptasensor based on designing and fabrication of a magnetic gold nanocomposite. Electroanalysis 30 2160–2166. 10.1002/elan.201800158 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

