Pulsed Electric Field Treatment Promotes Lipid Extraction on Fresh Oleaginous Yeast Saitozyma podzolica DSM 27192
- PMID: 33015025
- PMCID: PMC7516276
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.575379
Pulsed Electric Field Treatment Promotes Lipid Extraction on Fresh Oleaginous Yeast Saitozyma podzolica DSM 27192
Abstract
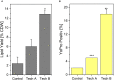
This study reports on the use of pulsed electric field (PEF) as a pre-treatment step to enhance lipid extraction yield using extraction with ethanol-hexane blend on fresh oleaginous yeast Saitozyma podzolica. The yeasts were cultivated on nitrogen-depleted condition and had a lipid content of 26.4 ± 4.6% of dry weight. PEF-treatment was applied on the yeast suspension either directly after harvesting (unwashed route) or after a washing step (washed route) which induced a reduction of conductivity by a factor eight. In both cases, cell concentration was 20 g of biomass per liter of suspension. In the unwashed route, the lipid extraction efficiency increased from 7% (untreated) to 54% thanks to PEF-treatment. In case an additional washing step was added after PEF-treatment, up to 81% of the lipid content could be recovered. The washed route was even more efficient since lipid extraction yields increased from 26% (untreated) to 99% of total lipid. The energy input for the PEF-treatment never exceeded 150 kJ per liter of initial suspension. The best lipid recovery scenario was obtained using pulses of 1 μs, an electric field of 40 kV/cm and it required slightly less than 11 MJ/kgLIPID. This amount of energy can be further reduced by at least a factor five by optimizing the treatment and especially by increasing the concentration of the treated biomass. The process can be easily up-scaled and does not require any expensive handling of the biomass such as freezing or freeze-drying. These findings demonstrate the potential benefit of PEF-treatment in the downstream processing of oleaginous yeast. From a basic research point of view, the influence of conductivity on PEF energy requirements and extraction yields was examined, and results suggest a higher efficiency of PEF-treatment in terms of energy when treatment is performed at lower conductivity.
Keywords: electroporation; fresh biomass; lipid; oleaginous yeast; pulsed electric field; pulsed electric field assisted extraction; solvent extraction.
Copyright © 2020 Gorte, Nazarova, Papachristou, Wüstner, Leber, Syldatk, Ochsenreither, Frey and Silve.
Figures






References
-
- Aronsson K., Rönner U., Borch E. (2005). Inactivation of Escherichia coli, Listeria innocua and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in relation to membrane permeabilization and subsequent leakage of intracellular compounds due to pulsed electric field processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 99 19–32. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.07.012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barba F. J., Parniakov O., Pereira S. A., Wiktor A., Grimi N., Boussetta N., et al. (2015). Current applications and new opportunities for the use of pulsed electric fields in food science and industry. Food Res. Int. 77 773–798. 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.09.015 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

