In Search of Effective Treatments Targeting α-Synuclein Toxicity in Synucleinopathies: Pros and Cons
- PMID: 33015057
- PMCID: PMC7500083
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.559791
In Search of Effective Treatments Targeting α-Synuclein Toxicity in Synucleinopathies: Pros and Cons
Abstract
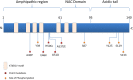
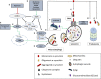
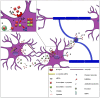
Parkinson's disease (PD), multiple system atrophy (MSA) and Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) represent pathologically similar, progressive neurodegenerative disorders characterized by the pathological aggregation of the neuronal protein α-synuclein. PD and DLB are characterized by the abnormal accumulation and aggregation of α-synuclein in proteinaceous inclusions within neurons named Lewy bodies (LBs) and Lewy neurites (LNs), whereas in MSA α-synuclein inclusions are mainly detected within oligodendrocytes named glial cytoplasmic inclusions (GCIs). The presence of pathologically aggregated α-synuclein along with components of the protein degradation machinery, such as ubiquitin and p62, in LBs and GCIs is considered to underlie the pathogenic cascade that eventually leads to the severe neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation that characterizes these diseases. Importantly, α-synuclein is proposed to undergo pathogenic misfolding and oligomerization into higher-order structures, revealing self-templating conformations, and to exert the ability of "prion-like" spreading between cells. Therefore, the manner in which the protein is produced, is modified within neural cells and is degraded, represents a major focus of current research efforts in the field. Given that α-synuclein protein load is critical to disease pathogenesis, the identification of means to limit intracellular protein burden and halt α-synuclein propagation represents an obvious therapeutic approach in synucleinopathies. However, up to date the development of effective therapeutic strategies to prevent degeneration in synucleinopathies is limited, due to the lack of knowledge regarding the precise mechanisms underlying the observed pathology. This review critically summarizes the recent developed strategies to counteract α-synuclein toxicity, including those aimed to increase protein degradation, to prevent protein aggregation and cell-to-cell propagation, or to engage antibodies against α-synuclein and discuss open questions and unknowns for future therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: autophagy; immunotherapy; propagation; proteasome; protein aggregation; synucleinopathies; therapeutics; α-synuclein.
Copyright © 2020 Fouka, Mavroeidi, Tsaka and Xilouri.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

