A Mutation in VWA1, Encoding von Willebrand Factor A Domain-Containing Protein 1, Is Associated With Hemifacial Microsomia
- PMID: 33015062
- PMCID: PMC7509151
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.571004
A Mutation in VWA1, Encoding von Willebrand Factor A Domain-Containing Protein 1, Is Associated With Hemifacial Microsomia
Abstract
Background: Hemifacial microsomia (HFM) is a type of rare congenital syndrome caused by developmental disorders of the first and second pharyngeal arches that occurs in one out of 5,600 live births. There are significant gaps in our knowledge of the pathogenic genes underlying this syndrome.
Methods: Whole exome sequencing (WES) was performed on five patients, one asymptomatic carrier, and two marry-in members of a five-generation pedigree. Structure of WARP (product of VWA1) was predicted using the Phyre2 web portal. In situ hybridization and vwa1-knockdown/knockout studies in zebrafish using morpholino and CRISPR/Cas9 techniques were performed. Cartilage staining and immunofluorescence were carried out.
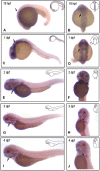
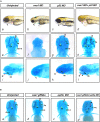
Results: Through WES and a set of filtration, we identified a c.G905A:p.R302Q point mutation in a novel candidate pathogenic gene, VWA1. The Phyre2 web portal predicted alterations in secondary and tertiary structures of WARP, indicating changes in its function as well. Predictions of protein-to-protein interactions in five pathways related to craniofacial development revealed possible interactions with four proteins in the FGF pathway. Knockdown/knockout studies of the zebrafish revealed deformities of pharyngeal cartilage. A decrease of the proliferation of cranial neural crest cells (CNCCs) and alteration of the structure of pharyngeal chondrocytes were observed in the morphants as well.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that a mutation in VWA1 is functionally linked to HFM through suppression of CNCC proliferation and disruption of the organization of pharyngeal chondrocytes.
Keywords: VWA1; cranial neural crest cell; hemifacial microsomia; whole exome sequencing; zebrafish.
Copyright © 2020 Wang, Ping, Luan, Chen, Fan, Li, Liu, Wang, Zhang, Zhang and Chen.
Figures
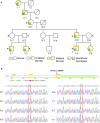
 indicates that whole-exome sequencing was done. (B) Sanger sequencing results of the VWA1 mutation in the pedigree. Patients III:1, IV:5, V:1, V:2 and V:4, and the asymptomatic carrier IV:1, all had the same non-synonymous point mutation (c.G905A:p.R302Q) in VWA1, whereas the two marry-in members of the family (IV:2 and IV:6) did not.
indicates that whole-exome sequencing was done. (B) Sanger sequencing results of the VWA1 mutation in the pedigree. Patients III:1, IV:5, V:1, V:2 and V:4, and the asymptomatic carrier IV:1, all had the same non-synonymous point mutation (c.G905A:p.R302Q) in VWA1, whereas the two marry-in members of the family (IV:2 and IV:6) did not.



References
-
- Allen J. M., Zamurs L., Brachvogel B., Schlötzer-Schrehardt U., Hansen U., Lamandé S. R., et al. (2009). Mice lacking the extracellular matrix protein WARP develop normally but have compromised peripheral nerve structure and function. J. Biol. Chem. 284 12020–12030. 10.1074/jbc.M806968200 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

