One Health in the context of coronavirus outbreaks: A systematic literature review
- PMID: 33015306
- PMCID: PMC7518973
- DOI: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2020.100170
One Health in the context of coronavirus outbreaks: A systematic literature review
Abstract
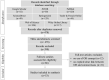
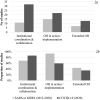
The ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic threatens global health thereby causing unprecedented social, economic, and political disruptions. One way to prevent such a pandemic is through interventions at the human-animal-environment interface by using an integrated One Health (OH) approach. This systematic literature review documented the three coronavirus outbreaks, i.e. SARS, MERS, COVID-19, to evaluate the evolution of the OH approach, including the identification of key OH actions taken for prevention, response, and control. The OH understandings identified were categorized into three distinct patterns: institutional coordination and collaboration, OH in action/implementation, and extended OH (i.e. a clear involvement of the environmental domain). Across all studies, OH was most often framed as OH in action/implementation and least often in its extended meaning. Utilizing OH as institutional coordination and collaboration and the extended OH both increased over time. OH actions were classified into twelve sub-groups and further categorized as classical OH actions (i.e. at the human-animal interface), classical OH actions with outcomes to the environment, and extended OH actions. The majority of studies focused on human-animal interaction, giving less attention to the natural and built environment. Different understandings of the OH approach in practice and several practical limitations might hinder current efforts to achieve the operationalization of OH by combining institutional coordination and collaboration with specific OH actions. The actions identified here are a valuable starting point for evaluating the stage of OH development in different settings. This study showed that by moving beyond the classical OH approach and its actions towards a more extended understanding, OH can unfold its entire capacity thereby improving preparedness and mitigating the impacts of the next outbreak.
Keywords: COVID-19; Collaboration; Disease ecology; MERS; One Health; SARS.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Emergency Committee Regarding the Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Geneva. 2005. Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations.https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-... Available:
-
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Coronaviruses. 2020. https://www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions/coronaviruses Available:
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous