Cross-Sectional Evaluation of Humoral Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Spike
- PMID: 33015650
- PMCID: PMC7524645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100126
Cross-Sectional Evaluation of Humoral Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Spike
Abstract
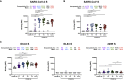
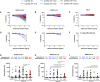
SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, infecting millions of people and causing hundreds of thousands of deaths. The Spike glycoproteins of SARS-CoV-2 mediate viral entry and are the main targets for neutralizing antibodies. Understanding the antibody response directed against SARS-CoV-2 is crucial for the development of vaccine, therapeutic, and public health interventions. Here, we perform a cross-sectional study on 106 SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals to evaluate humoral responses against SARS-CoV-2 Spike. Most infected individuals elicit anti-Spike antibodies within 2 weeks of the onset of symptoms. The levels of receptor binding domain (RBD)-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) persist over time, and the levels of anti-RBD IgM decrease after symptom resolution. Although most individuals develop neutralizing antibodies within 2 weeks of infection, the level of neutralizing activity is significantly decreased over time. Our results highlight the importance of studying the persistence of neutralizing activity upon natural SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; IgG; IgM; RBD; SARS-CoV-2; Spike glycoproteins; coronavirus; cross-reactivity, IgA; neutralization.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Cross-sectional evaluation of humoral responses against SARS-CoV-2 Spike.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jul 30:2020.06.08.140244. doi: 10.1101/2020.06.08.140244. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell Rep Med. 2020 Oct 20;1(7):100126. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100126. PMID: 32577637 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

