Role of a Pediatric Cardiologist in the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 33015722
- PMCID: PMC7533115
- DOI: 10.1007/s00246-020-02476-y
Role of a Pediatric Cardiologist in the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
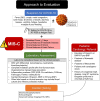
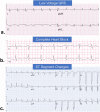
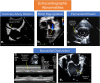
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has affected patients across all age groups, with a wide range of illness severity from asymptomatic carriers to severe multi-organ dysfunction and death. Although early reports have shown that younger age groups experience less severe disease than older adults, our understanding of this phenomenon is in continuous evolution. Recently, a severe multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), with active or recent COVID-19 infection, has been increasingly reported. Children with MIS-C may demonstrate signs and symptoms of Kawasaki disease, but also have some distinct differences. These children have more frequent and severe gastrointestinal symptoms and are more likely to present with a shock-like presentation. Moreover, they often present with cardiovascular involvement including myocardial dysfunction, valvulitis, and coronary artery dilation or aneurysms. Here, we present a review of the literature and summary of our current understanding of cardiovascular involvement in children with COVID-19 or MIS-C and identifying the role of a pediatric cardiologist in caring for these patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cardiovascular; MIS-C; Pediatric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose. Authors have indicated they have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Global Surveillance for human infection with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) https://www.who.int/publications-detail/global-surveillance-for-human-in.... Accessed 1 June 2020
-
- Shekerdemian LS, Mahmood NR, Wolfe KK, Riggs BJ, Ross CE, McKiernan CA, Heidemann SM, Kleinman LC, Sen AI, Hall MW, Priestley MA, McGuire JK, Boukas K, Sharron MP, Burns JP, Collaborative ftIC-P Characteristics and outcomes of children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection admitted to US and Canadian pediatric intensive care units. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1948. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

