Analysis of virulence traits of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis in semi-intensive and family dairy farms
- PMID: 33016022
- PMCID: PMC7533384
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2020.21.e77
Analysis of virulence traits of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis in semi-intensive and family dairy farms
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus is one of the main microorganisms that causes bovine mastitis, and its well-known virulence characteristics and interactions with the environment are used to aid the design of more efficient therapies.
Objectives: To determine whether the virulence traits, such as antibiotic resistance and biofilm-forming and internalization abilities, of S. aureus isolated from bovine mastitis are related to dairy production system types.
Methods: The study was performed in the Mexican states of Guanajuato and Michoacan. Semi-intensive dairy farms (SIDFs) and family dairy farms (FDFs) (454 and 363 cows, respectively) were included. The 194 milk samples from mastitis affected quarters were collected and 92 strains of S. aureus were isolated and identified by biochemical and molecular tests. Antibiotic resistance, biofilm and internalization assays were performed on 30 randomly selected isolated strains to determine virulence traits, and these strains were equally allocated to the 2 dairy production systems.
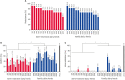
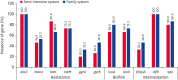
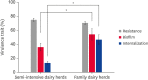
Results: All 30 selected strains displayed a high degree of resistance (50%-91.7%) to the antibiotics tested, but no significant difference was found between SIDF and FDF isolates. S. aureus strains from SIDFs had an average biofilm forming capacity of up to 36% (18.9%-53.1%), while S. aureus strains from FDFs registered an average of up to 53% (31.5%-77.8%) (p > 0.05). Internalization assays revealed a higher frequency of internalization capacity for strains isolated from FDFs (33.3%) than for those isolated from SIDFs (6.7%) (p > 0.05). fnbpA gen was detected in 46.6% of FDF strains and 33.3% of SIDF strains, and this difference was significant (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Our findings show that the virulence traits of S. aureus isolates analyzed in this study, depend significantly on several factors, such as phenotype, genotype, and environmental conditions, which are significantly related to dairy production system type and daily management practices.
Keywords: Dairy system; Staphylococcus aureus; biofilm; internalization; multi-resistance.
© 2020 The Korean Society of Veterinary Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Argaw A. Review on epidemiology of clinical and subclinical mastitis on dairy cows. Food Sci Qual Manag. 2016;52(6):56–65.
-
- Thiran E, Di Ciccio PA, Graber HU, Zanardi E, Ianieri A, Hummerjohann J. Biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus dairy isolates representing different genotypes. J Dairy Sci. 2018;101(2):1000–1012. - PubMed
-
- Dhanawade NB, Kalorey DR, Srinivasan R, Barbuddhe SB, Kurkure NV. Detection of intercellular adhesion genes and biofilm production in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine subclinical mastitis. Vet Res Commun. 2010;34(1):81–89. - PubMed
-
- Pereyra EA, Picech F, Renna MS, Baravalle C, Andreotti CS, Russi R, et al. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus adhesion and biofilm-producing genes and their expression during internalization in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Vet Microbiol. 2016;183:69–77. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

