TRIM31 promotes apoptosis via TAK1-mediated activation of NF-κB signaling in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction
- PMID: 33016203
- PMCID: PMC7644163
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1826235
TRIM31 promotes apoptosis via TAK1-mediated activation of NF-κB signaling in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction
Abstract
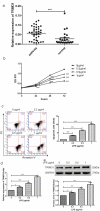
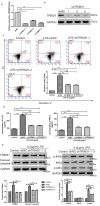
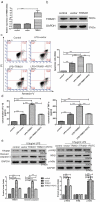
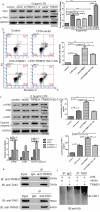
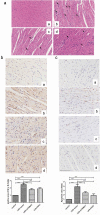
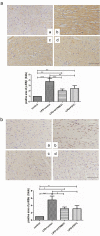
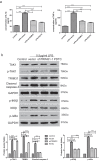
Sepsis is a major condition caused by an overwhelming inflammatory response to an infection. Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction (SIMD) is a common complication in septic patients and a major predictor of morbidity and mortality. Here, we investigated the role of tripartite motif 31 (TRIM31) protein in sepsis progression in vitro and in vivo. Quantitative real-time PCR and western blot were used to detect the expression levels of relative genes and proteins. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were evaluated to determine cell viability. H&E and IHC staining were performed to examine morphological and pathological changes in mice. ELISA assay was used to detect inflammatory factors. TRIM31 was upregulated in septic patients compared with normal people. TRIM31 depletion reduced LPS-induced apoptosis whereas TRIM31 overexpression-elevated LPS-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, TRIM31 interacted with and ubiquitinated transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase-1 (TAK1), resulting in TAK1 activation and subsequent induction of NF-κB signaling. Of note, Trim31 depletion or blockade by PDTC treatment inhibited LPS-induced apoptosis in vivo. In conclusion, TRIM31 played an important role in SIMD by activating TAK1-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: NF-κB; TAK1; TRIM31; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM31 plays a critical role in hypertensive nephropathy by promoting proteasomal degradation of MAP3K7 in the TGF-β1 signaling pathway.Cell Death Differ. 2022 Mar;29(3):556-567. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00874-0. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Cell Death Differ. 2022. PMID: 34584221 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic TRIM31 confers gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer via activating the NF-κB signaling pathway.Theranostics. 2018 May 11;8(12):3224-3236. doi: 10.7150/thno.23259. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29930725 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 18 negatively regulates and inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis by targeting transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 activity.Int Immunol. 2021 Aug 23;33(9):461-468. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxab029. Int Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34423815
-
TAK1 control of cell death.Cell Death Differ. 2014 Nov;21(11):1667-76. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.123. Epub 2014 Aug 22. Cell Death Differ. 2014. PMID: 25146924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM31: A potential therapeutic target.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jul;176:116846. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116846. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38850648 Review.
Cited by
-
The E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Trim31 alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by targeting Rhbdf2 in mouse hepatocytes.Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 25;13(1):1052. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28641-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35217669 Free PMC article.
-
Matairesinol exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in sepsis-mediated brain injury by repressing the MAPK and NF-κB pathways through up-regulating AMPK.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Oct 27;13(20):23780-23795. doi: 10.18632/aging.203649. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34705665 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment with interleukin-15 attenuates inflammation and apoptosis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction.Eur J Histochem. 2024 Apr 29;68(2):4019. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2024.4019. Eur J Histochem. 2024. PMID: 38686889 Free PMC article.
-
miR-361-3p overexpression promotes apoptosis and inflammation by regulating the USP49/IκBα/NF-κB pathway to aggravate sepsis-induced myocardial injury.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Nov 19;13(6):tfae190. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae190. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39568464
-
Loss of Trim31 Worsens Cardiac Remodeling in a Mouse Model of Heart Failure by Enhancing the Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):2650-2662. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02217-w. Epub 2024 Dec 13. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39673012
References
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, et al. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Flynn A, Chokkalingam Mani B, Mather PJ. Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: a review of pathophysiologic mechanisms. Heart Fail Rev. 2010;15:605–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
