Structural analysis, virtual screening and molecular simulation to identify potential inhibitors targeting 2'-O-ribose methyltransferase of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus
- PMID: 33016237
- PMCID: PMC7544923
- DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1828172
Structural analysis, virtual screening and molecular simulation to identify potential inhibitors targeting 2'-O-ribose methyltransferase of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus
Abstract
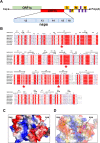
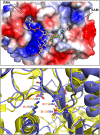
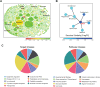
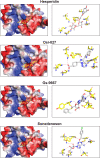
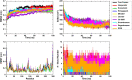
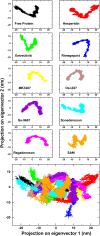
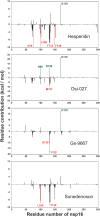
SARS-CoV-2, an emerging coronavirus, has spread rapidly around the world, resulting in over ten million cases and more than half a million deaths as of July 1, 2020. Effective treatments and vaccines for SARS-CoV-2 infection do not currently exist. Previous studies demonstrated that nonstructural protein 16 (nsp16) of coronavirus is an S-adenosyl methionine (SAM)-dependent 2'-O-methyltransferase (2'-O-MTase) that has an important role in viral replication and prevents recognition by the host innate immune system. In the present study, we employed structural analysis, virtual screening, and molecular simulation approaches to identify clinically investigated and approved drugs which can act as promising inhibitors against nsp16 2'-O-MTase of SARS-CoV-2. Comparative analysis of primary amino acid sequences and crystal structures of seven human CoVs defined the key residues for nsp16 2-O'-MTase functions. Virtual screening and docking analysis ranked the potential inhibitors of nsp16 from more than 4,500 clinically investigated and approved drugs. Furthermore, molecular dynamics simulations were carried out on eight top candidates, including Hesperidin, Rimegepant, Gs-9667, and Sonedenoson, to calculate various structural parameters and understand the dynamic behavior of the drug-protein complexes. Our studies provided the foundation to further test and repurpose these candidate drugs experimentally and/or clinically for COVID-19 treatment.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Keywords: KDKE motif; SARS-CoV-2; inhibitor; methyltransferase; molecular dynamics simulation; nsp16; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal, V., Tuli, H. S., Thakral, F., Singhal, P., Aggarwal, D., Srivastava, S., Pandey, A., Sak, K., Varol, M., Khan, M. A., & Sethi, G. (2020). Molecular mechanisms of action of hesperidin in cancer: Recent trends and advancements. Experimental Biology and Medicine (Maywood, N.J.).), 245(5), 486–497. 10.1177/1535370220903671 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aouadi, W., Blanjoie, A., Vasseur, J. J., Debart, F., Canard, B., & Decroly, E. (2017). Binding of the methyl donor S-adenosyl-l-methionine to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2'-O-methyltransferase nsp16 promotes recruitment of the allosteric activator nsp10. Journal of Virology, 91(5), e02217-16. 10.1128/JVI.02217-16 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
