Inhibition properties of free and conjugated leupeptin analogues
- PMID: 33016476
- PMCID: PMC7714073
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.12994
Inhibition properties of free and conjugated leupeptin analogues
Abstract
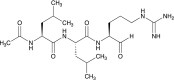
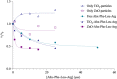
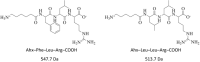
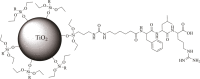
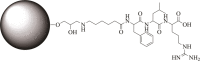
Leupeptin is a naturally occurring inhibitor of various proteases, in particular serine proteases. Following its discovery, the inhibitory properties of several other peptidyl argininals have been studied. The specificity of leupeptin is most likely due to the Leu-Leu-Argininal sequence, and its C-terminal aldehyde group has been suggested to enhance the binding efficiency and to be essential for function. The terminal aldehyde group makes the structure less vulnerable to carboxypeptidases. Here, we investigated whether the inhibitory function of leupeptin toward serine proteases is retained after oxidation or reduction of the aldehyde group. The oxidized form, which corresponds to the natural precursor, was shown to be superior to the reduced form in terms of inhibitory properties. However, the original leupeptin possessed enhanced inhibitory properties as compared with the oxidized form. Based on these results, new synthetic leupeptin analogues, 6-aminohexanoic acid (Ahx)-Phe-Leu-Arg-COOH and Ahx-Leu-Leu-Arg-COOH, were prepared by solid-phase peptide synthesis using the Fmoc strategy. In these analogues, the N-terminal capping acetyl group was replaced with a 6-aminohexanoyl group to allow conjugation. The structures of the modified leupeptin and the synthetic peptides were confirmed by mass spectrometry. Determination of the inhibitory properties against trypsin (IEC 3.4.21.4, Chymotrypsin IEC 3.4.21.1) revealed that these further modified tripeptides were tight binding inhibitors to their target enzyme, similar to the naturally occurring leupeptin, with Ki values generally in the micromolar range. The Ahx-Phe-Leu-Arg-COOH analogue was selected for conjugation to inorganic oxide nanoparticles and agarose gel beads. All conjugates exhibited inhibitory activity in the same range as for the free peptides.
Keywords: conjugation; inhibition; inhibitor design; leupeptin analogues; tight binding.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



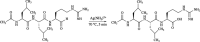

References
-
- Maeda K, Kawamura K, Hondo S, Aoyagi T, Takeuchi T and Umezawa H (1971) The structure and activity of leupeptins and related analogs. J Antibiotics 24, 402–404. - PubMed
-
- Aoyagi T, Miyata S, Nanbo M, Kojima F, Matsuzaki M, Ishizuka M, Takeuchi T and Umezawa H (1969) Biological activities of leupeptins. J Antibiot 22, 558–568. - PubMed
-
- Toyo‐oko T, Shimizu T and Masaki T (1978) Inhibition of proteolytic activity of calcium activated neutral protease by leupeptin and antipain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 82, 484–491. - PubMed
-
- Tamura Y, Hirado M, Okamura K, Minato Y and Fujii S (1977) Synthetic inhibitors of trypsin, plasmin, kallikrein, thrombin, C1r, and C1 esterase. Biochem Biophys Acta 484, 417–422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

