The association of interieukin-6 polymorphism (rs1800795) with microvascular complications in Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 33016995
- PMCID: PMC7569201
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20201105
The association of interieukin-6 polymorphism (rs1800795) with microvascular complications in Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the effects of the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs1800795 in interieukin-6 (IL-6) gene on diabetic microvascular complications of Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), using statistical meta-analysis.
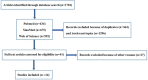
Methods: Literature pertaining to the relationship between the SNP rs1800795 and microvascular complications of T2DM including diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic neuropathy and foot disease was retrieved from PubMed, Web of Science Knowledge and SinoMed databases. Original information was analyzed using Stata 12.0, including meta-analysis statistics, test for heterogeneity, evaluation of publication bias and sensitivity. Subgroup analysis was conducted to assess the effect of specific factors on the corresponding results.
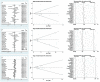
Results: In total, 14 eligible articles were obtained. The SNP rs1800795 in IL-6 gene is not correlated with risk of microvascular complications in T2DM. Among the original literature, a genetic model (OR = 1.071, 95% CI: 0.681-1.685, P=0.767), an allelic genetic model (OR = 1.010, 95% CI: 0.959-1.063, P=0.703), a heterozygote genetic model (OR = 1.107, 95% CI: 0.916-1.339, P=0.292), a dominant genetic model (OR = 1.108, 95% CI: 0.885-1.387, P=0.372), and a recessive genetic model (OR = 0.978, 95% CI: 0.646-1.478, P=0.917) were included respectively. In the subgroup analysis by types of diabetic microvascular complications, we found no correlation between the SNP rs1000795 polymorphism and complications of T2DM in either the homozygote genetic model or the allelic genetic model (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that rs1800795 polymorphism in IL-6 gene is not correlated with the susceptibility of microvascular complications of T2DM.
Keywords: Diabetic microvascular complications; Gene polymorphism; Interleukin-6 gene; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; rs1800795.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Nadeem A., Mumtaz S., Naveed A.K. et al. (2017) Association of IL-6 C-174G (rs 1800795) single nucleotide polymorphism with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Pakistani population. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 67, 428–433 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

