Sprr2f protects against renal injury by decreasing the level of reactive oxygen species in female mice
- PMID: 33017192
- PMCID: PMC7789986
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00318.2020
Sprr2f protects against renal injury by decreasing the level of reactive oxygen species in female mice
Abstract
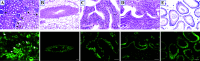
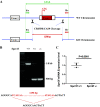
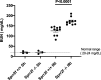
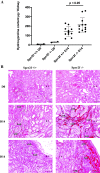
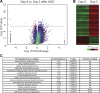
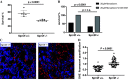
Renal injury leads to chronic kidney disease, with which women are not only more likely to be diagnosed than men but have poorer outcomes as well. We have previously shown that expression of small proline-rich region 2f (Sprr2f), a member of the small proline-rich region (Sprr) gene family, is increased several hundredfold after renal injury using a unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) mouse model. To better understand the role of Sprr2f in renal injury, we generated a Sprr2f knockout (Sprr2f-KO) mouse model using CRISPR-Cas9 technology. Sprr2f-KO female mice showed greater renal damage after UUO compared with wild-type (Sprr2f-WT) animals, as evidenced by higher hydroxyproline levels and denser collagen staining, indicating a protective role of Sprr2f during renal injury. Gene expression profiling by RNA sequencing identified 162 genes whose expression levels were significantly different between day 0 and day 5 after UUO in Sprr2f-KO mice. Of the 162 genes, 121 genes were upregulated after UUO and enriched with those involved in oxidation-reduction, a phenomenon not observed in Sprr2f-WT animals, suggesting a protective role of Sprr2f in UUO through defense against oxidative damage. Consistently, bilateral ischemia-reperfusion injury resulted in higher serum blood urea nitrogen levels and higher tissue reactive oxygen species in Sprr2f-KO compared with Sprr2f-WT female mice. Moreover, cultured renal epithelial cells from Sprr2f-KO female mice showed lower viability after oxidative damage induced by menadione compared with Sprr2f-WT cells that could be rescued by supplementation with reduced glutathione, suggesting that Sprr2f induction after renal damage acts as a defense against reactive oxygen species.
Keywords: acute renal injury; chronic renal injury; ischemia-reperfusion injury; reactive oxygen species; small proline-rich region 2f.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Collecting Duct-Specific CR6-Interacting Factor-1-Deletion Aggravates Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis Induced by Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 28;22(21):11699. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111699. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769136 Free PMC article.
-
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells conditioned medium attenuate interstitial fibrosis and stimulate the repair of tubular epithelial cells in an irreversible model of unilateral ureteral obstruction.Nephrology (Carlton). 2018 Aug;23(8):728-736. doi: 10.1111/nep.13099. Nephrology (Carlton). 2018. PMID: 28667820
-
Identification of Candidate Genes Involved in Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.DNA Cell Biol. 2019 Mar;38(3):256-262. doi: 10.1089/dna.2018.4551. Epub 2019 Jan 22. DNA Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30668132 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and regulation of reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) in renal tubular epithelial cells.Am J Pathol. 2010 Dec;177(6):2765-73. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100199. Epub 2010 Oct 22. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20971739 Free PMC article.
-
Role of protease-activated receptor 4 in mouse models of acute and chronic kidney injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Feb 1;326(2):F219-F226. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00162.2023. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38031732 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Single-cell analysis reveals urothelial cell heterogeneity and regenerative cues following cyclophosphamide-induced bladder injury.Cell Death Dis. 2021 May 5;12(5):446. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03740-6. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33953164 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Selected Small Proline-Rich Proteins in Tissue Homogenates from Samples of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;15(13):1633. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15131633. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647632 Free PMC article.
-
Loricrin at the Boundary between Inside and Outside.Biomolecules. 2022 May 6;12(5):673. doi: 10.3390/biom12050673. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35625601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TcrXY is an acid-sensing two-component transcriptional regulator of Mycobacterium tuberculosis required for persistent infection.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 22;15(1):1615. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45343-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38388565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson KR, Haeussler M, Watanabe C, Janakiraman V, Lund J, Modrusan Z, Stinson J, Bei Q, Buechler A, Yu C, Thamminana SR, Tam L, Sowick MA, Alcantar T, O’Neil N, Li J, Ta L, Lima L, Roose-Girma M, Rairdan X, Durinck S, Warming S. CRISPR off-target analysis in genetically engineered rats and mice. Nat Methods 15: 512–514, 2018. doi:10.1038/s41592-018-0011-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

